In today’s technological era, anyone can reach anything out there, even though they are in different countries. Therefore, for your website or business owners, it is important to ensure that people from outside your country can still reach it.
One way is to provide website multilingual content. When your website is multilingual, it is important to ensure that your website is indexed by search engines, so that visitors can find it when they make a search query in their language.
Then, how to index automatic translation on a website? And what tools can help you to translate a website? Check out the explanation in this article.
Understanding automatic translation and indexing
Before entering this topic, we can discuss what is automatic translation and indexing. Automatic translation, also known as machine translation, is the process of using computer algorithms and technology to automatically translate text or speech from one language to another.
It involves utilizing advanced linguistic and statistical models to analyze and generate translations without human intervention.
The advantages of automatic translation include
- Efficiency in translating content
- Cost-effectiveness
- Consistent translation results
- Capable of being used to translate large amounts of content
- Allows quick translation of content into multiple languages
On the other hand, indexing refers to the process of organizing and categorizing content to make it searchable and discoverable by search engines. When it comes to multilingual websites, indexing involves ensuring that all translated versions of the website’s content are appropriately indexed by search engines.
This allows users to search in different languages to find the relevant content in their preferred language.
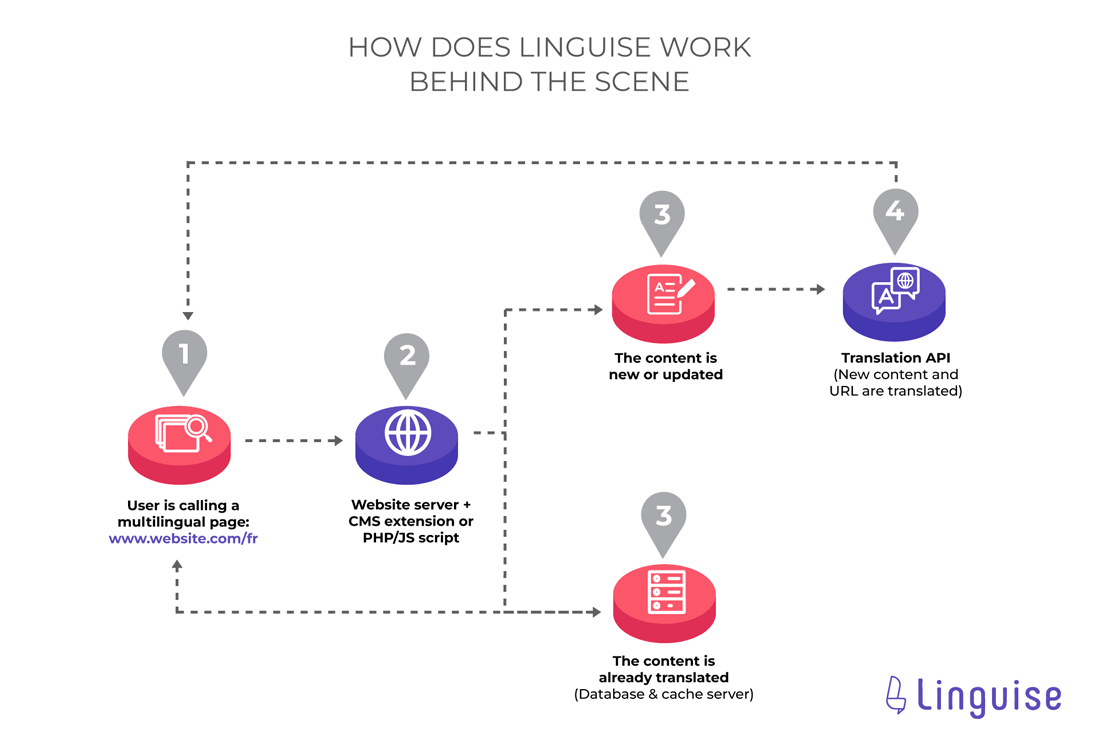
Here’s a quick graphic about how the automatic translation is generated on all the major translation tool on the market, Linguise included.

How to index automatic translation on a website?
After understanding what automatic translation is, its advantages, and what indexing is, now is the time for us to go into how to index automatic translation on a website. There are several ways that need to be done to index automatic translation on websites.
1. Managing language variations and hreflang tags
Hreflang tags are a technique used in multilingual website development to indicate to search engines the language and regional targeting of different versions of a page. The hreflang tag is an HTML attribute that helps search engines understand the language preference and geotargeting of a particular page, so they can serve users the most relevant version based on their location and language preference.
The hreflang tag is added to the head of a page and consists of two main components: the hreflang attribute and the language/region code. The hreflang attribute defines the relationship between the different language or region versions of the page, while the language/region code identifies the language and region-specific to each version.
Here’s an example of a hreflang implementation tag for a French page (“FR”):
<html lang="fr" dir="ltr" class="wf-montserrat-n4-active wf-montserrat-n7-active wf-active" data-lt-installed="true" data-inboxsdk-session-id="1686904917791-0.7698031234432856">
2. Canonical URLs for multilingual pages
The second way for website translation results to be indexed is to use a canonical URL/ Canonical URL is the URL that is selected as the main URL or the “original” URL of a web page. This is used to address duplicate content issues that may occur on typical or multilingual websites by having multiple versions of a URL displaying the same or very similar content.
When a page has more than one URL pointing to the same content, search engines like Google can consider it as duplicate content. This can negatively impact a page’s ranking in search results, as search engines may allocate their resources to indexing multiple versions that are actually the same.
By using the rel=”canonical” tag, you can inform search engines that the specified URL is the canonical URL which should be considered the primary URL.
On multilingual websites, provide the canonical tag on the page with the original or default language version. Below is an example of using the canonical URL.
<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.linguise.com/fr/blog/guide/comment-configurer-la-console-de-recherche-google-pour-les-sites-web-multilingues/">
3. Submit translated pages to search engines
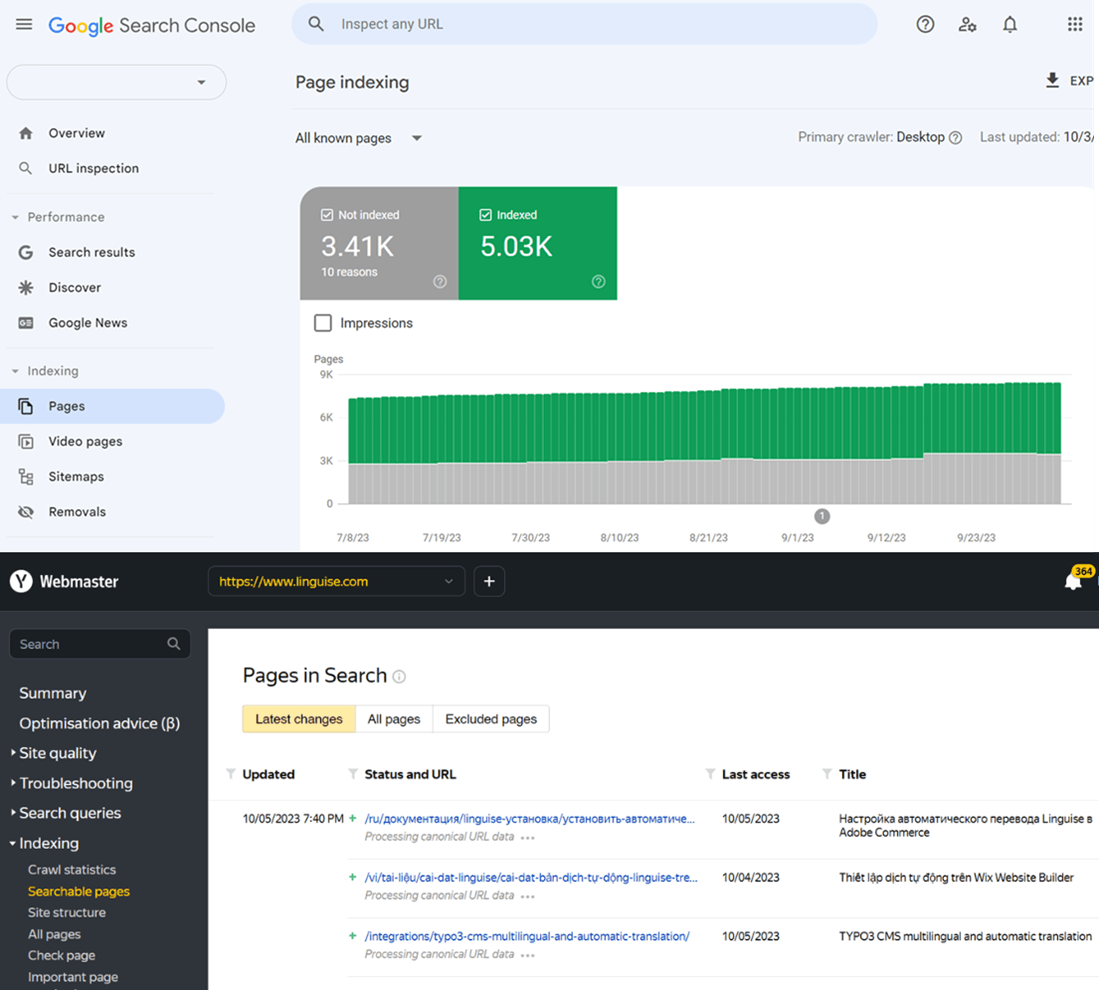
The third way is to submit translated pages to search engines via webmaster tools, like Google Search Console. If your website has separate URLs for different language versions, be sure to submit each translated URL to search engines. This helps search engines understand the multilingual nature of your website and index language-specific pages accordingly.
To submit each translated page you can use Google Search Console, if you don’t know how, here are the steps you can follow.
- Login to Google Search Console with your Google account
- Verify website ownership
- Add the property (website) and verify each language version
- Click inspenct any URL
- Submit translated URLs
- Check indexing status
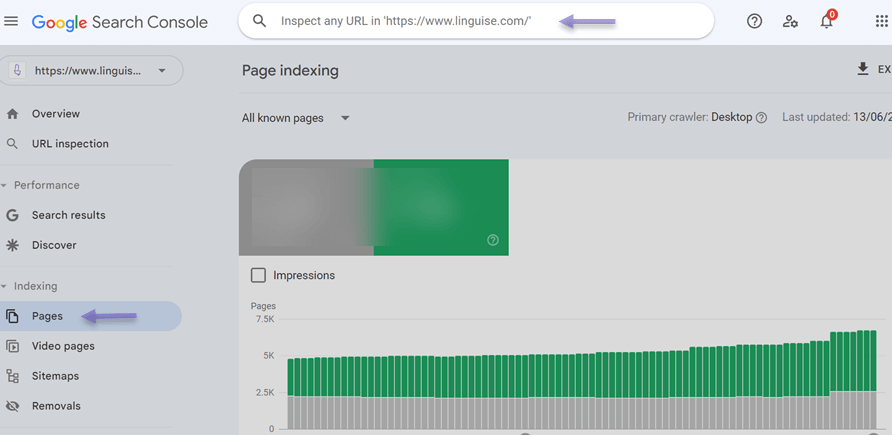

By submitting translated URLs to search engines through webmaster tools, you help search engines recognize and index the pages in the appropriate language versions. This will improve the visibility and ranking of your website in search results for users searching in the respective languages.
4. Add a link to the translated version
The fourth step so that translations can be indexed is by linking between other available translation pages. This will further strengthen the relationship between the pages. For example:
<rule name="Linguise language redirection" stopProcessing="true">
<match url="^(af|sq|am|ar|hy|az|eu|be|bn|bs|bg|ca|ceb|ny|zh-cn|zh-tw|co|hr|cs|da|nl|en|eo|et|tl|fi|fr|fy|gl|ka|de|el|gu|ht|ha|haw|iw|hi|hmn|hu|is|ig|id|ga|it|ja|jw|kn|kk|km|ko|ku|ky|lo|la|lv|lt|lb|mk|mg|ms|ml|mt|mi|mr|mn|my|ne|no|ps|fa|pl|pt|pa|ro|ru|sm|gd|sr|st|sn|sd|si|sk|sl|so|es|su|sw|sv|tg|ta|te|th|tr|uk|ur|uz|vi|cy|xh|yi|yo|zu|zz-zz)(?:$|/)(.*)$" />
<action type="Rewrite" url="/wp-content/plugins/linguise/script.php?linguise_language={R:1}&original_url={R:2}" appendQueryString="true" />
</rule>
5. Optimizing meta tags and descriptions
Optimizing meta tags and descriptions on a multilingual website requires some additional considerations to ensure that each language version is effectively optimized. Translate the meta tags (including title tags and meta descriptions) for each language version of your website. Ensure that the translations accurately reflect the content and purpose of each page. It’s important to provide unique and language-specific meta tags and descriptions for each language version.
Besides that, don’t forget to consider cultural nuances and preferences when optimizing meta tags and descriptions for different languages. Pay attention to local idioms, expressions, and sensitivities to ensure that the messaging resonates with the target audience.
6. Utilizing XML sitemaps for multilingual content
Utilizing XML sitemaps for multilingual content refers to the practice of creating and submitting XML sitemaps specifically designed for websites that have multiple language versions. XML sitemaps are structured files that provide search engines with information about the pages on your website, helping them understand and index your content more effectively.
Utilizing XML sitemaps involves generating separate sitemaps for each language version. These sitemaps include the URLs of the pages in their respective languages, along with language annotations such as hreflang tags. Hreflang tags indicate the language and regional targeting of each page, ensuring that search engines associate the correct language version with the appropriate audience.
By utilizing XML sitemaps for multilingual content, you improve the visibility and accessibility of your language-specific pages to search engines. It helps search engines discover and crawls your multilingual content more efficiently, increasing the chances of your website appearing in relevant search results for different language queries.
Submitting the XML sitemaps to search engines through their webmaster tools is a crucial step. It notifies the search engines about the existence of multiple language versions and provides them with the necessary information to crawl and index your multilingual content accurately.
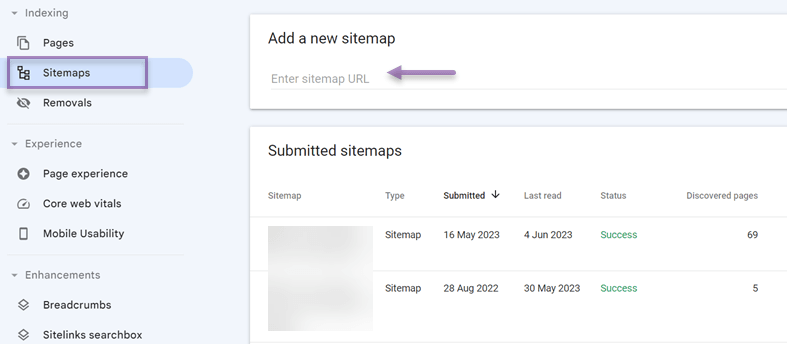

To find out how to submit an XML sitemap for multilingual content, you can check this article How to setup the Google Search Console for multilingual websites.
Linguise, index automatic translation on your website
Apart from knowing how to index automatic translations on websites, it is also important to use an automatic translation service for websites. Because this will support your website index process.
Make sure you choose an automatic translation service that supports multilingual SEO, so that it can help you index page translations.
One of the translation service providers is Linguise. Linguise is an automatic translation service or multilingual plugin that can help you in indexing because Linguise supports 100% SEO.
Linguise respects all search engine recommendations regarding multilingual SEO like.
- Use hreflang generation.
- Alternative URLs
- Default language tags
- Canonical URLs for multilingual pages
- XML sitemaps translation
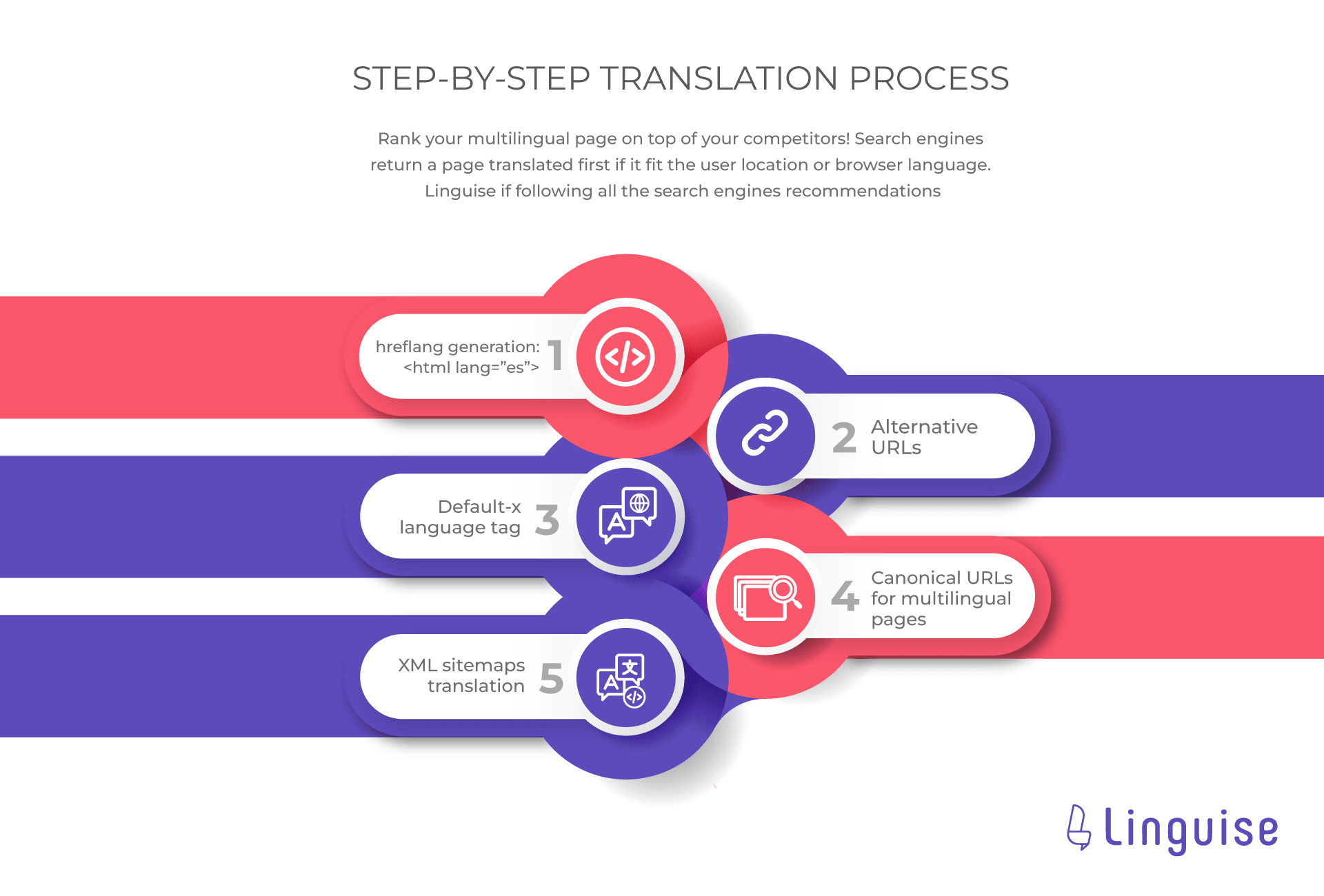

Moreover, Linguise multilingual content is fully and quickly indexed by all major search engines as it has been tested on all search engine webmaster tools.
The Linguise translation tool can also generate an XML sitemap based on your main website’s sitemap, and it updates automatically when bots display and index your new multilingual content.
Thus, Linguise is able to help translated pages on websites to be indexed by search engines and appear in searches.
Conclusion
Now you know how to index automatic translations on websites. Indexing translated pages is one of the important things in implementing SEO to help improve website performance.
When pages are successfully indexed and found by audiences, more and more audiences from various countries will visit your site.
If you are interested in using Linguise, immediately register for a free Linguise account and use the trial version for the next 1 month. Of course with the various features offered such as translating up to 600 thousand words without any language usage restrictions!