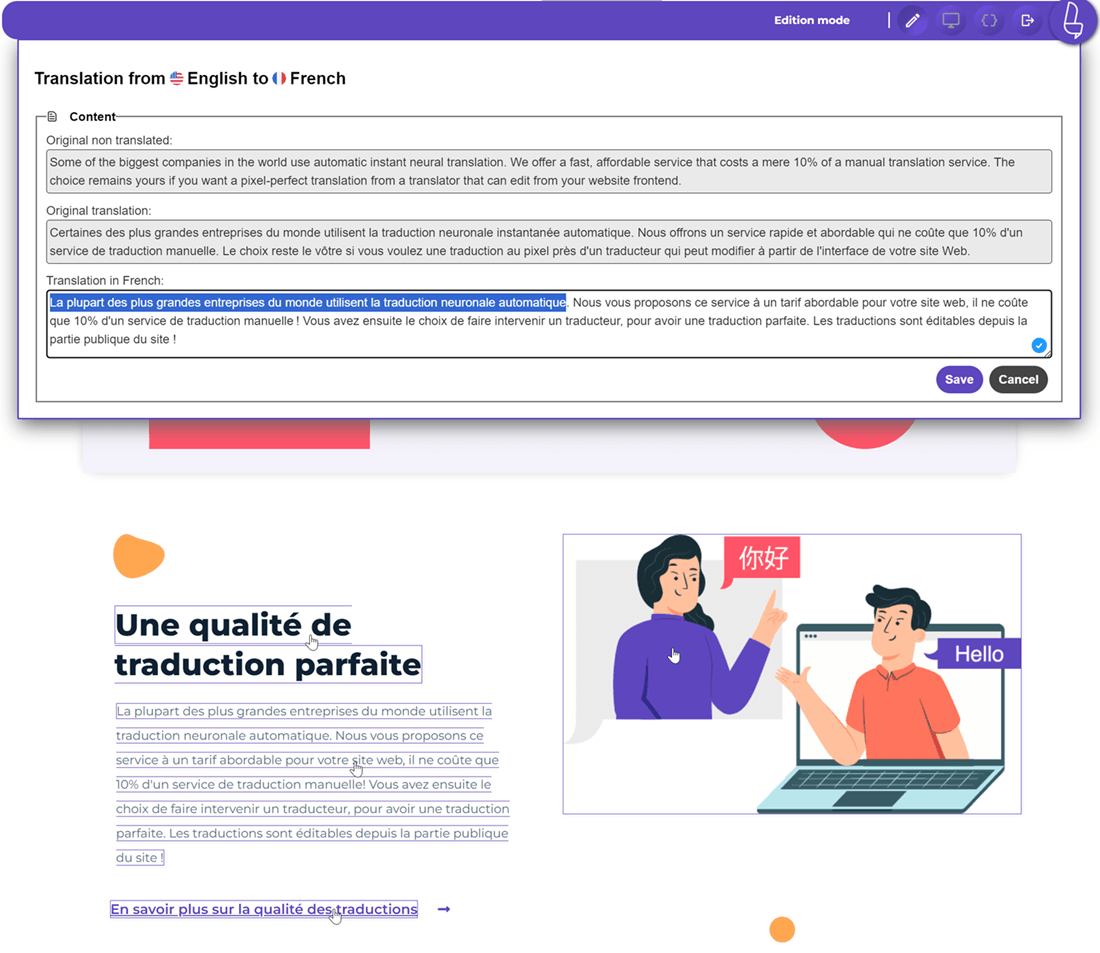
Korean web translation is crucial for global businesses to reach South Korea’s digitally active market. However, translating a website into Korean involves more than word accuracy, it demands attention to the language’s structure, cultural tone, and technical aspects unique to Hangul. Mistranslation or formatting issues can easily disrupt user experience or distort your brand message.
To succeed, businesses must anticipate challenges such as handling the Korean honorific system, managing text expansion, and optimizing for Naver, Korea’s dominant search engine. This guide explores common translation problems, cultural nuances, and best practices to ensure your Korean website delivers linguistic accuracy and user trust.
Understanding the complexity of the Korean honorific system

One of the biggest hurdles in Korean website translation is navigating the honorific system, a linguistic feature deeply rooted in social hierarchy and respect. Unlike English, Korean communication changes based on the speaker’s relationship with the listener, age, or social position. This makes accurate translation especially challenging for automated systems, which often fail to grasp subtle differences in tone and formality. To understand why this matters, let’s break it down into three key layers:
- 존댓말 (Jondaetmal) – The formal and polite speech level used in professional or customer-facing communication. For example, eCommerce sites and service platforms addressing customers must use this form to maintain respect and professionalism.
- 반말 (Banmal) – The informal speech style typically used among close friends or peers. Using it on a corporate website can appear rude or dismissive to Korean users.
- Honorific verbs and endings – Many Korean verbs change depending on your address. Automated translation tools often miss these nuances, producing phrases that feel unnatural or even offensive.
Businesses should use a glossary of formal expressions, ensure native speaker proofreading, and adopt translation systems that account for social context. These practices preserve brand credibility and help build trust with Korean audiences, who are highly sensitive to language tone and respect.
Common problems in Korean web translation

Translating a website into Korean comes with unique technical challenges beyond words. Even with accurate translations, text encoding, layout, and interface design issues can disrupt user experience and make a site look unprofessional. Below are some of the most common technical problems businesses face when localizing their websites for Korean audiences.
Encoding and font compatibility problems
Korean text uses Hangul characters, which require proper encoding, such as UTF-8. If a website uses incompatible fonts or encoding, users may see garbled text, question marks, or boxes instead of characters. This is especially common when integrating third-party plugins or content from multiple sources.
Ensuring font compatibility and correct encoding is crucial for readability and maintaining a professional appearance. Choosing web-safe fonts that fully support Hangul and testing across different platforms can prevent these issues.
Text expansion and layout breaks

Korean words and sentences can be longer than their English counterparts, which often causes text to overflow or disrupt existing layouts. Buttons, menus, and content boxes may not accommodate the expanded text, resulting in a broken or cramped design.
To address this, designers should implement flexible layouts and responsive design principles that adapt to longer strings. Using CSS techniques like min-width and max-width and testing text in real-world scenarios helps maintain a clean appearance.
Line spacing and alignment issues
The visual structure of Korean text can differ significantly from Latin-based languages. Line spacing may appear too tight or uneven without proper attention, and text alignment can look off, especially in multi-column layouts or headers.
Adjusting line height and alignment for Hangul ensures that text is readable and visually balanced. Regular QA testing on various devices and browsers is necessary to spot and fix these subtle but noticeable formatting issues.
Broken UI elements in dynamic content

Dynamic content, such as pop-ups, sliders, or interactive menus, can break after translation if the system does not account for Hangul’s text length or character behavior. Buttons may be cut off, dropdowns misaligned, or animations disrupted.
Developers should test dynamic components thoroughly after localization, and consider using scalable containers that adjust automatically to text length. Collaboration between translators and UI developers is key to maintaining functionality.
Inconsistent rendering across devices and browsers
Even if text and layouts are correctly implemented, Korean content may render differently on various devices and browsers. Differences in font rendering engines or operating systems can make the same page appear inconsistent, affecting readability and brand perception.
Cross-device and cross-browser testing is essential to ensure a consistent user experience. Using web-safe fonts, responsive design, and fallback options for unsupported fonts helps maintain a uniform appearance across all platforms.
Cultural nuances that machine translation often misses

Machine translation can handle literal word-for-word conversion, but it often fails to capture the Korean language’s subtle cultural and contextual layers. Misunderstanding these nuances can lead to awkward phrasing, miscommunication, or even offense, which is why human oversight is critical in Korean website localization.
Misinterpretation of honorifics and politeness level
Korean honorifics and politeness levels are essential in establishing respect and social hierarchy. Automated translation tools often misapply 존댓말 (formal) and 반말 (informal) forms, resulting in messages that may seem disrespectful or overly stiff.
Businesses must ensure that customer-facing content consistently uses the correct level of formality. Native speaker review or specialized translation software that recognizes context helps maintain appropriate tone and professionalism.
Literal translation of idioms and local expressions

Korean idioms and cultural expressions rarely translate directly into English or other languages. Literal translations can confuse readers or convey unintended meanings. For example, a phrase that works humorously in English may appear nonsensical or offensive in Korean.
To avoid this, translators should adapt idiomatic content to culturally equivalent expressions. This preserves the intended meaning and keeps the text natural and engaging for Korean users.
Gender sensitivity and social context in the Korean Language
Korean language carries implicit gender cues, and some phrases or pronouns can unintentionally signal bias. Machine translation may overlook these subtleties, producing content that feels insensitive or exclusionary.
Localization teams should review content for gender neutrality where appropriate and ensure that wording aligns with contemporary social norms in Korea. This approach fosters inclusivity and protects brand reputation.
Overlooking regional dialects and informal speech patterns
Korean has various regional dialects (사투리, saturi) and informal speech patterns that influence tone and comprehension. Automated tools often standardize language, ignoring local preferences or colloquial nuances.
Adapting content to the target audience’s regional and informal context can enhance relatability. For example, marketing campaigns may incorporate familiar expressions to connect authentically with specific demographics.
Ignoring cultural references and emotional tone
Cultural references, humor, and emotional cues in Korean often get lost in automated translation. Content may appear flat, confusing, or emotionally off-key, reducing engagement and trust.
Human post-editing and cultural review ensure that messaging resonates emotionally with Korean users. Maintaining the right tone strengthens user trust and enhances overall website experience.
SEO optimization for Korean search engines like Naver
Optimizing a website for Korean search engines requires a different approach than for Google. Naver, Korea’s dominant search platform, prioritizes localized content, user engagement, and community-driven platforms. Businesses targeting Korean audiences must adapt content and technical SEO strategies to align with Naver’s ecosystem.
Conducting effective keyword research for the Korean market
Keyword research for Naver goes beyond literal translation of English terms. Korean users often search using colloquial expressions, slang, or romanized words. Tools like Naver Keyword Planner and Naver Keyword Trend helps identify the most relevant search terms and analyze how their popularity changes.
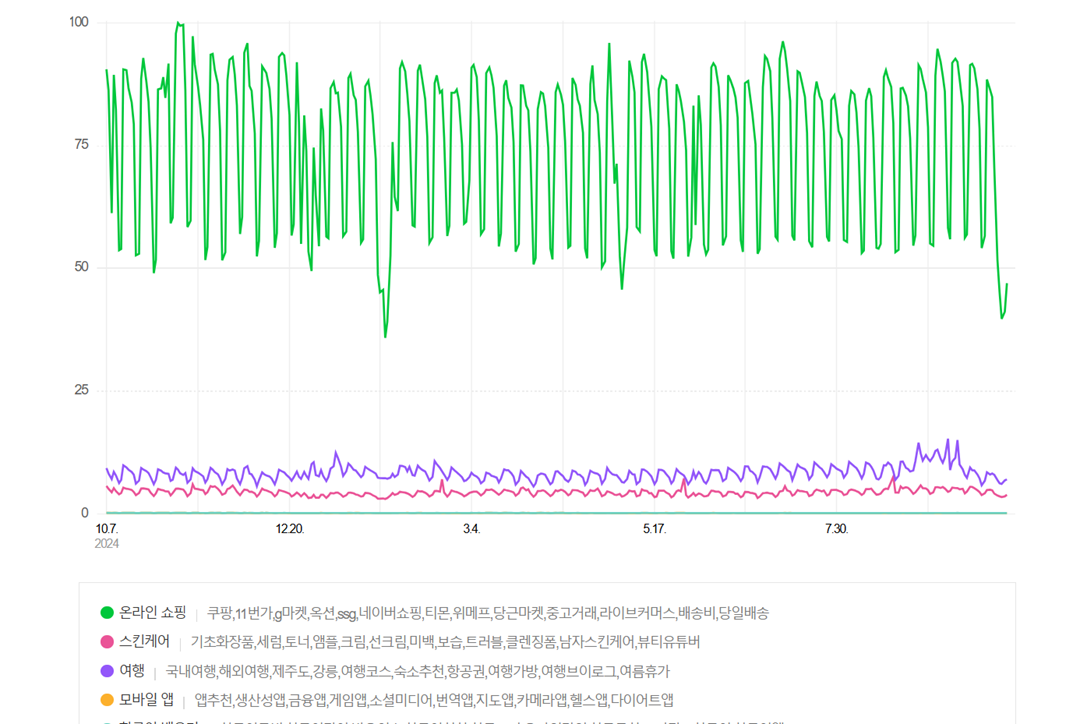
For instance, businesses can compare keywords such as “온라인 쇼핑,” “스킨케어,” or “여행” to track seasonal trends and adjust their content accordingly. This approach allows brands to align their SEO strategies with real-time user interests, ensuring visibility and engagement on Naver.
Optimizing on-page elements for Naver visibility
Naver values well-structured on-page SEO elements such as titles, meta descriptions, headings, and category tags. Unlike Google, excessive backlinks are less influential. Naver SEO focuses more on content readability, keyword placement, and how well pages serve user intent within the Korean context. Optimizing these on-page factors helps improve visibility across Naver’s diverse search sections, including blogs, news, and shopping results.
For instance, a product page for skincare should include clear meta descriptions in Korean with relevant keywords, headings that organize the content logically, and structured HTML that Naver can easily index. Incorporating Naver SEO practices like using localized keywords and maintaining natural language flow helps the page rank higher in search results and appear prominently in Naver’s preview snippets.
Leveraging Naver blog and Café for content distribution
Naver Blog and Naver Café remain two of the most influential platforms for boosting organic visibility and credibility in South Korea. Many Korean users rely on Naver’s integrated search results, where blog posts often appear alongside web pages and news articles. These platforms are essential for content distribution, especially for brands looking to connect with niche communities and generate authentic engagement.
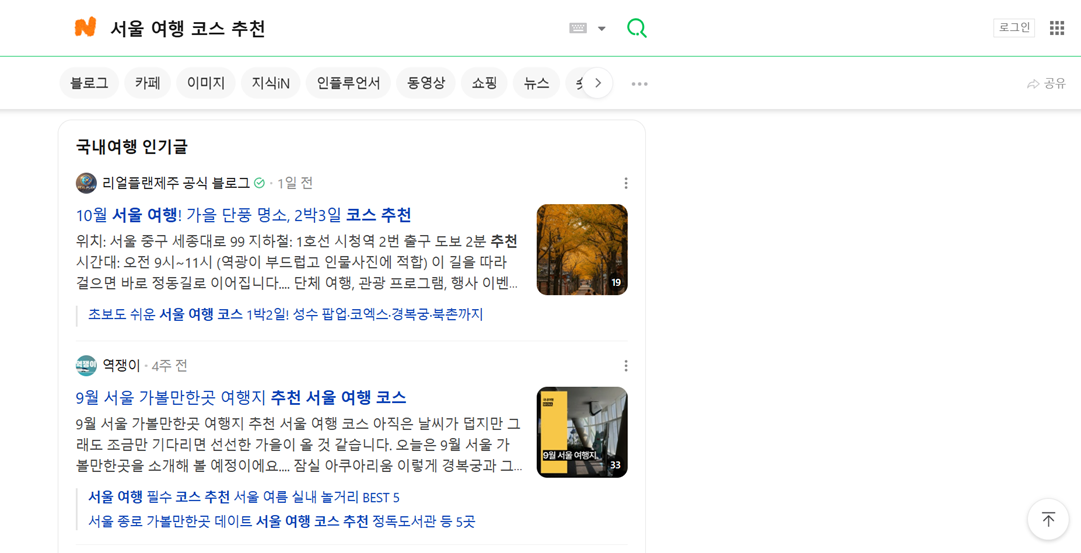
For example, when users search for “서울 여행 코스 추천” (Seoul travel course recommendations), blog posts featuring travel itineraries, photos, and reviews often dominate the top results. A travel agency can use this by publishing optimized blog content that includes local tips, route suggestions, and internal links to their main website. This approach drives traffic and builds brand trust and authority within Korea’s highly active online ecosystem.
Analyze organic traffic with Naver Analytics
Tracking performance on Naver requires analyzing user behavior, top pages, and search queries using Naver Analytics. Metrics such as session duration, bounce rate, and click-through rate indicate how well content resonates with Korean users.
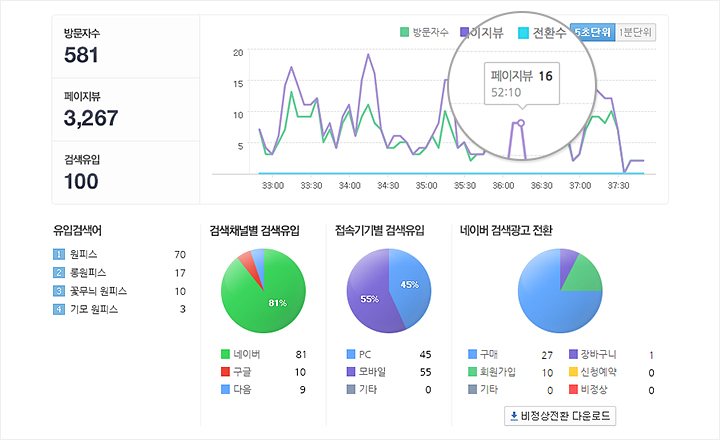
For example, if a fashion eCommerce site notices that product pages receive high impressions but low clicks, it may indicate that meta descriptions or product titles need adjustment. Continuous analysis allows businesses to refine content and improve engagement.
Monitor ranking trends and keyword performance
Regularly monitoring keyword rankings and search trends on Naver helps businesses stay competitive. Naver’s algorithm updates frequently, and user search behavior can change seasonally or by trend.
For instance, a tech retailer may notice a surge in searches for “무선 이어폰” (wireless earphones) during holiday seasons. Adjusting content and promotions according to these trends ensures that pages remain relevant and maintain high visibility.
Best practices for Korean website translation

To achieve both linguistic accuracy and cultural relevance, Korean website translation should combine the strengths of technology and human expertise. Beyond word conversion, businesses need structured workflows and quality control to ensure that every update or content change aligns with Korean users’ expectations and maintains SEO performance.
Combine automation with human post-editing
Automation accelerates translation, especially for websites with large or frequently updated content. However, machine output alone can’t grasp Korean’s complex honorifics or cultural nuances. Human post-editing ensures the tone, style, and accuracy remain consistent with the brand’s voice.
For example, an eCommerce platform using AI translation can combine automated workflows with a solution like Linguise to handle real-time translation updates through its front live editor. This feature allows translators to review and adjust text directly on the website interface, ensuring accuracy and cultural fit. Native Korean linguists can then refine tone and honorifics, resulting in fast yet natural translations that align with both brand voice and audience expectations.
Implement continuous localization for dynamic content
Continuous localization is essential for websites that frequently update, such as eCommerce platforms, news sites, or service-based applications. This approach ensures that every new product, article, or announcement is automatically translated and published in real-time, keeping all language versions consistent. By integrating localization directly into the content workflow, businesses can maintain up-to-date information for Korean audiences without manual intervention or long delays.
This method also helps preserve layout structure, formatting, and SEO metadata when updates occur. Continuous localization allows global and Korean versions of a site to evolve together, providing users with a seamless experience regardless of language.
Maintain consistency with glossaries and style guides
Consistency is key in building brand credibility, especially in languages like Korean, where multiple terms may exist for the same concept. Creating a translation glossary and style guide helps translators and editors maintain uniformity across all pages.
For instance, a software company should decide whether to translate “dashboard” as “대시보드” (daesibodeu) or keep it in English. Once standardized, these terms should remain consistent across user interfaces, documentation, and marketing materials.
Conduct regular QA and UX testing
Translation accuracy is only part of the equation, user experience must also be tested after localization. Regular QA and UX testing ensure that translated content displays properly, functions correctly, and feels intuitive for Korean users.
For example, a translated checkout page should be tested for text overflow, button alignment, and currency formatting. Gathering user feedback can reveal subtle usability issues that automated checks may overlook, helping maintain both performance and customer trust.
Conclusion
Korean website translation requires more than linguistic precision, it demands a deep understanding of Korea’s cultural, linguistic, and digital ecosystem. From navigating the intricate honorific system to ensuring technical compatibility and SEO alignment with Naver, every detail plays a crucial role in shaping user trust and engagement. Businesses that treat translation as localization, not just text conversion, will stand out in South Korea’s competitive online market.
Combining automated translation tools with native-level human editing, consistent terminology, and continuous localization is key. By adopting a solution like Linguise, businesses can automate multilingual updates while maintaining quality and SEO performance, ensuring their Korean website feels authentic, culturally relevant, and optimized for long-term success.