Voice search trends in Southeast Asia are changing how users interact with content, requiring technical SEO to adapt to local linguistic and cultural behaviors. As conversational, question-based queries grow, businesses must stay visible by optimizing for these patterns.
Cultural and multilingual nuances, like code-switching, local slang, and dialect variations, impact how searches are interpreted. SEO strategies should focus on natural language, long-tail queries, and proper technical setups such as schema markup and multilingual indexing.
Adoption trends and key markets for voice search in Southeast Asia

The trend of voice search adoption in Southeast Asia shows significant growth, reflecting changes in consumer behavior that increasingly rely on voice technology in everyday life. Countries such as Indonesia, Thailand, the Philippines, and Vietnam are the main markets driving this trend, supported by increasing internet penetration and a tech-savvy young population. Digital Market data shows users increasingly switch from text to voice search, focusing on complete sentences and conversational phrases.
According to Demand Sage data, approximately 20.5% of global internet users utilize voice search, with the total number of active voice assistants reaching 8.4 billion units by 2025. Although no specific data is available in Southeast Asia, this global trend indicates that the region contributes significantly to this growth.
Major technology companies such as Google, Amazon, and Microsoft have increased their investments in Southeast Asia, reflecting their confidence in the market’s potential. For example, Google announced a $2 billion investment to build data centers and cloud services in Malaysia, which will support voice-based search services.
Thus, despite challenges such as language and dialect diversity, the market potential for voice search in Southeast Asia is enormous, and companies that can tailor their strategies to meet local needs will have a significant competitive advantage.
Cultural and multilingual nuances that shape voice queries
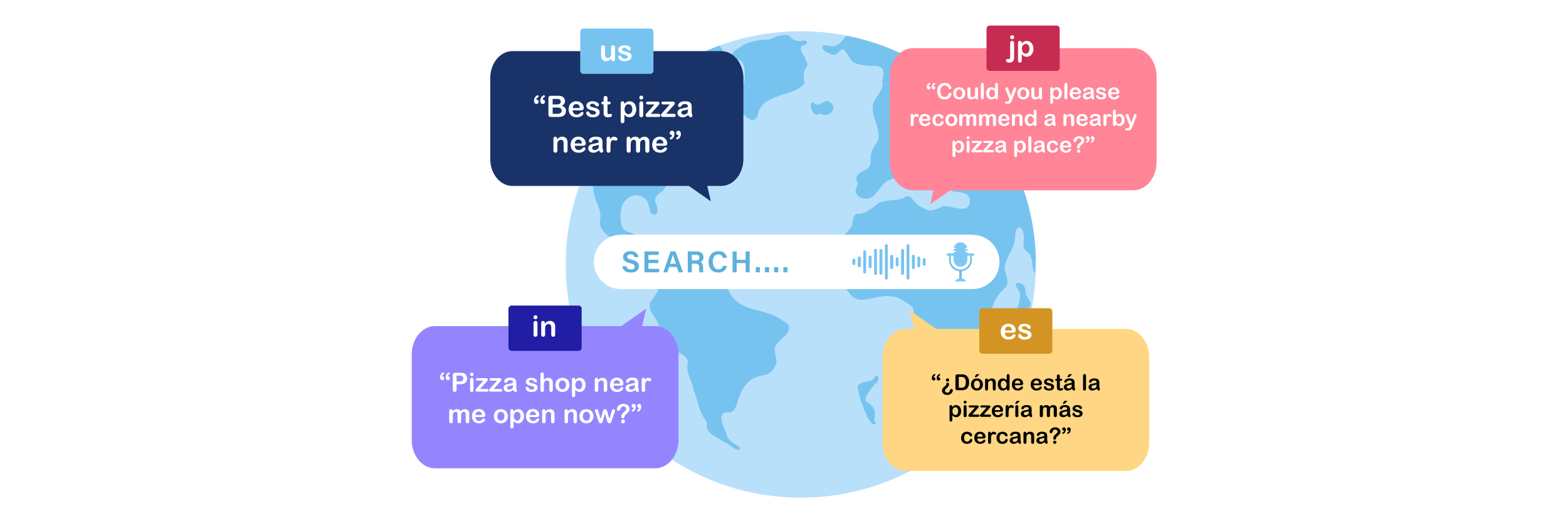
Cultural and linguistic diversity deeply influences voice search behavior in Southeast Asia. Users often combine languages, dialects, and informal speech in ways that reflect daily communication patterns, which creates unique challenges for search engines in accurately interpreting queries. Understanding these nuances is crucial for optimizing content for voice search.
Code-switching in everyday speech
In Southeast Asia, it is common for people to switch between languages mid-sentence, such as combining the local language with English. This code-switching occurs naturally in conversation and affects how search engines interpret voice queries. A query may contain keywords from two languages, making it important for content to address both.
SEO strategies should incorporate mixed-language phrases in key content, headings, and metadata. Recognizing the common code-switching patterns ensures that queries in either language can retrieve relevant results, improving overall visibility and user satisfaction.
Dialects, accents, and informal language patterns
Regional dialects and accents can significantly alter pronunciation, leading to misinterpretation in voice recognition systems. Informal speech, including contractions or local expressions, adds another layer of complexity. Search engines may struggle to correctly match these queries to standard content.
To address this, content creators can include alternative spellings, phonetic variations, or colloquial terms within content and metadata. This approach helps ensure voice queries from diverse regions are properly understood and matched, enhancing search accuracy across audiences.
Mixing English with local slang in queries

Many users blend English words with local slang in their searches, particularly in tech, entertainment, or product-related topics. For example, a user might say, “Best gadget murah di Jakarta,” combining English and Indonesian. Ignoring these hybrid forms can lead to missed search opportunities.
Optimizing content for voice search requires identifying commonly used slang and including them alongside standard language terms. This allows search engines to match conversational queries more effectively, improving the likelihood of appearing in results for hybrid-language searches.
Shortened phrases vs. full-sentence queries
Unlike typed searches, voice queries often come as full sentences rather than single keywords. Users may ask, “Where can I find cheap nasi lemak in Kuala Lumpur?” instead of typing “cheap nasi lemak KL.” This shift toward more conversational phrasing changes how content should be structured to provide direct answers.
To adapt, content should offer concise, natural-language responses and include question-based headings or FAQ sections. Framing answers in full-sentence form increases the likelihood that voice assistants can extract and deliver accurate results to users.
Use of polite forms and honorifics in local languages
In some Southeast Asian languages, such as Thai or Javanese, users include polite forms or honorifics in their voice queries. This is especially common when speaking to devices perceived as “formal” or in public settings. Ignoring these forms can reduce search accuracy.
Content creators should consider including respectful terms or alternate forms where relevant. This helps match user intent, ensuring that queries containing polite language still lead to accurate and relevant results.
Religious and cultural terminology in search intent

Users often incorporate religious or cultural terms when making voice searches, reflecting local customs, holidays, or rituals. Queries may include phrases like “Ramadan recipe” or “Bali temple opening hours,” which may not appear in standard SEO keyword research.
Including culturally relevant terminology and context in content helps align with these user intents. Businesses and content creators can improve visibility by anticipating culturally influenced queries and providing direct answers within content tailored to local contexts.
Variations in pronunciation that affect ASR
Automatic speech recognition (ASR) can misinterpret words due to regional or age-related pronunciation differences. For example, a word pronounced in Jakarta may sound slightly different in Surabaya or Penang, potentially causing errors in voice query matching.
To mitigate this, content creators can account for common pronunciation variants, include phonetic spellings, or use FAQ-style content that mirrors natural speech. This ensures that voice queries are correctly understood and matched to relevant content, improving search effectiveness across diverse user groups.
Technical SEO challenges in voice search

Voice search introduces unique technical SEO challenges because queries are often longer, conversational, and multilingual. Ensuring content is discoverable, correctly indexed, and structured for direct answers requires careful optimization. Businesses must adapt their SEO strategies to meet these evolving demands.
Handling long-tail and conversational queries
Voice queries are typically longer than typed searches and often take the form of natural sentences. This creates challenges for SEO because standard keyword targeting may not cover the variety of ways users phrase their questions. Content that only targets short keywords may miss valuable traffic from voice searches.
The screenshot below shows the difference between text-based searches, such as “cheap hotel bali” and voice searches with complete sentences such as “Where can I find a cheap hotel in Bali for 2 nights?”.
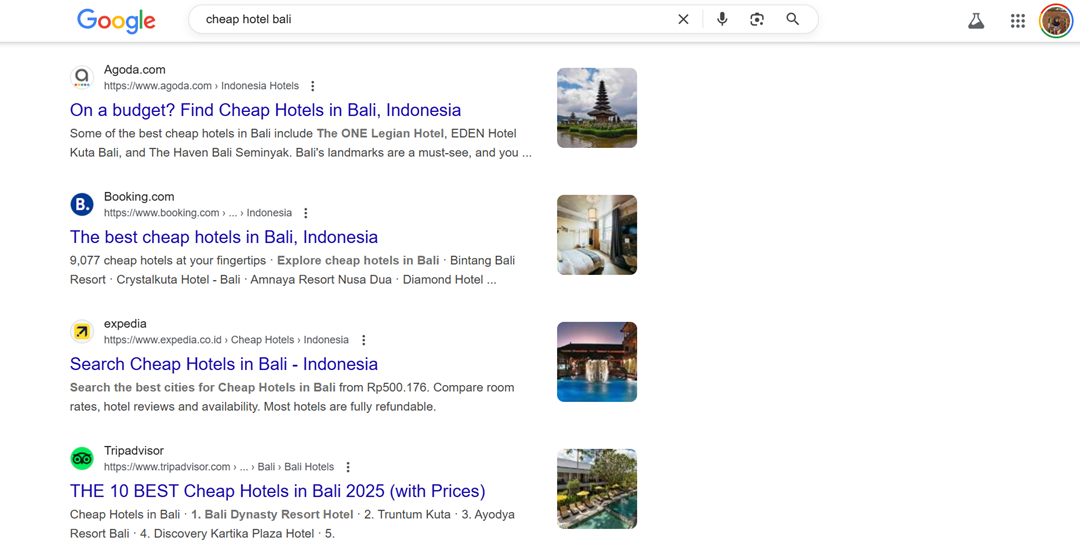
Although both have the same intent, the language structure is very different, and if content is only optimized for short keywords, conversational search results like this can be missed.
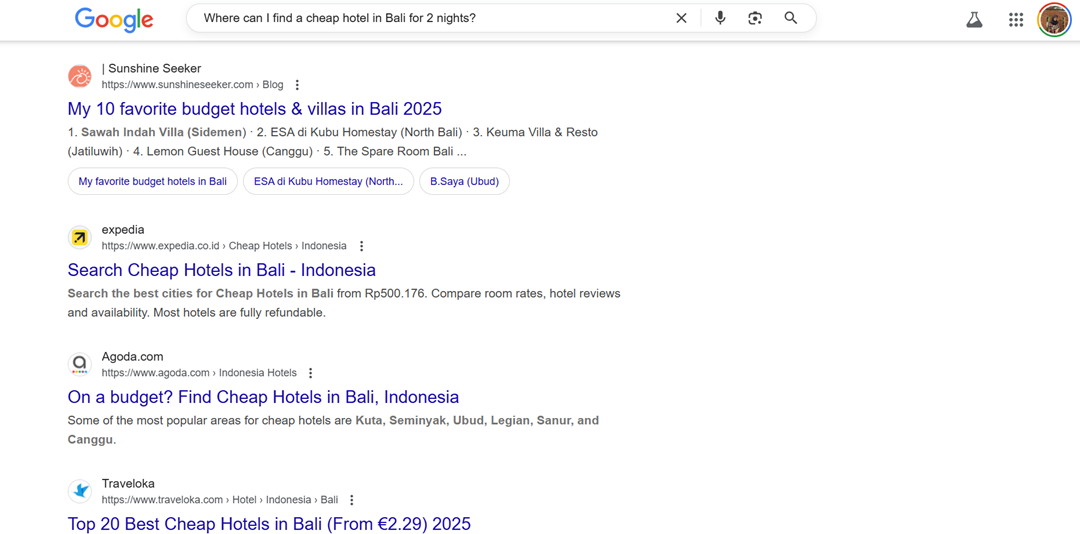
To address this, websites should integrate long-tail keywords that reflect full-sentence queries. Analyzing real user queries and updating content to include conversational language helps search engines better match queries to relevant pages, improving visibility for voice search.
Structuring content for direct answers
Voice assistants favor content that provides clear, concise answers. One challenge is structuring information to be easily extracted and read aloud. Voice search platforms may overlook pages with dense paragraphs or unclear formatting.
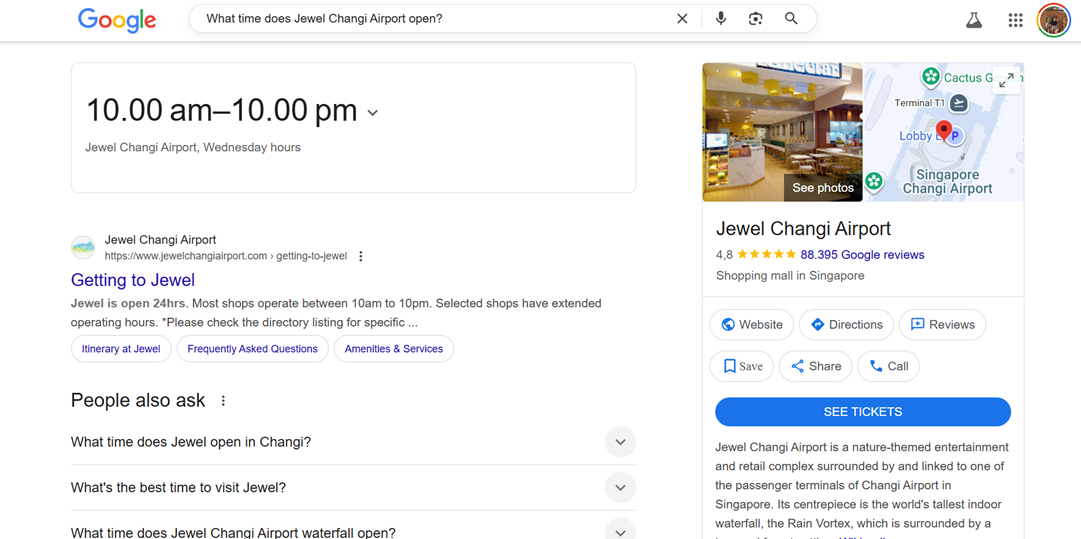
Using headings, bullet points, and short paragraphs helps content stand out as a direct answer. FAQ sections and highlighted summaries make it easier for search engines to identify the most relevant information, improving the chances of being featured in voice responses. For example, when one of the following keywords, “What time does Jewel Changi Airport open?” is searched on Google, a snippet of opening hours and relevant FAQs will immediately appear.
Optimizing for question-based search patterns
Many voice searches are framed as questions like “How do I get to Tanah Lot temple?” Traditional SEO often focuses on keywords rather than question intent, limiting visibility. This creates the challenge of predicting and optimizing for various possible queries.
To overcome this, content should be crafted to include question-and-answer formats. Using headings that mimic common questions and naturally integrating answers ensures that voice queries are accurately matched to content, improving search relevance.
Improving crawlability and indexability across languages
Multilingual content adds complexity to technical SEO for voice search. Ensuring that search engines can crawl and index pages in multiple languages is challenging, especially when sites use different URLs or subdomains for localized content.
Proper hreflang tags, language-specific sitemaps, and clean URL structures help search engines understand the language and regional targeting. This improves indexability and ensures users get the most relevant results in their preferred language.
Managing duplicate content across localized versions

Duplicate content can occur when similar pages are created in different languages or regions. This is a major challenge because search engines may struggle to determine which version to rank, reducing visibility for voice searches. Using canonical tags and ensuring each localized page provides unique, relevant content helps mitigate this issue. Proper content differentiation ensures that voice queries are directed to the most appropriate page, maintaining user experience and search performance.
However, managing this manually across dozens of language versions can be time-consuming.
A translation and localization solution like Linguise automatically generates SEO-friendly URLs, applies canonical tags, and ensures each translated version is treated as a unique page rather than duplicate content, allowing businesses to scale multilingual voice search optimization without risking indexation conflicts.
Schema markup coverage for voice-driven SERPs
Voice search often relies on structured data to identify relevant answers quickly. A challenge is ensuring schema markup is implemented consistently across pages, including multilingual content and localized versions.
Using schema types, such as FAQ, HowTo, and Product, makes it easier for search engines to extract information for voice responses. Regular auditing and structured data updates help maintain accuracy and improve visibility in voice-driven search results.
Content strategy for voice search optimization

Optimizing content for voice search requires a shift from traditional SEO practices. Because voice queries are conversational and often question-based, content must be structured to answer questions naturally, be easily digestible, and reflect real user intent. A strategic approach ensures that content is discoverable and ranks well for voice queries.
Optimize for natural language and question-based keywords
Voice search queries are often phrased in full sentences rather than short keywords. This makes it essential to target natural language phrases and question-based keywords like “Where can I find the best coffee in France?” instead of simply “best coffee France.”
Including these phrases in headings, FAQs, and body text helps search engines match conversational queries. For example, a travel website can create a FAQ page answering, “What are the top attractions in Ubud?” to target voice search traffic directly.
Localize content beyond translation

Users often search in their native language and expect culturally relevant content. Simply translating content is not enough; localization content should adapt examples, currency, measurements, and context to local customs.
For instance, a recipe site targeting Malaysia should use local ingredient names and measurements familiar to Malaysian users rather than literal translations. This approach improves engagement and ensures that voice search returns meaningful results.
Create voice-friendly formats
Content should be structured so that voice assistants can easily read aloud. Short paragraphs, bullet points, numbered steps, and clear headings help voice assistants extract information efficiently.
For example, a guide on “How to Visit Gardens by the Bay” with numbered directions from Bayfront MRT and key tips in bullet points allows users to receive concise spoken instructions, enhancing usability for voice search.
Use a conversational tone without losing authority

Voice search users expect a natural, easy-to-understand tone. However, content should also maintain credibility and authority, especially for technical, health, or financial topics. Writing too casually may weaken trust, while writing too formally may sound robotic, so the key is striking the right balance between conversational and informative.
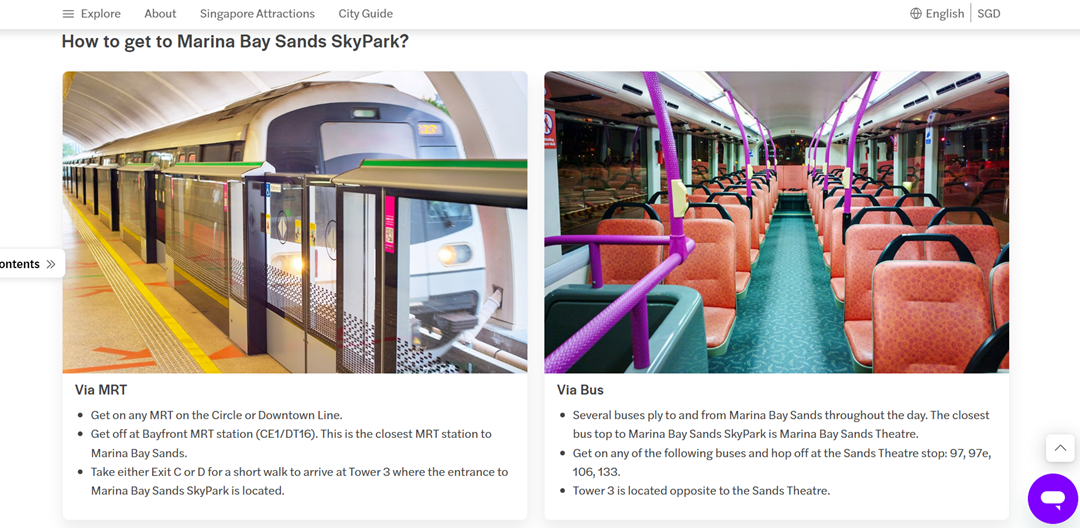
Instead of describing directions to a place like Marina Bay Sands in long paragraphs, breaking the instructions into short, sequential steps makes it far easier for human readers and voice assistants to process. Screenshot-based guides such as “How to Go to Marina Bay Sands via MRT” presented in bullet points or numbered lists work exceptionally well. Not only are they scannable on mobile, but when read aloud by Google Assistant or Siri, the instructions remain clear and actionable.
Align content with real-life search scenarios
Immediate needs or everyday situations often drive voice queries. Understanding common search contexts helps create content that directly addresses user intent.
For example, a restaurant website in Singapore can include content answering the question, “Which halal restaurants are open near Orchard Road after 9 PM?” This ensures users get practical answers that fit real-life situations, improving the likelihood of voice search engagement.
Conclusion
Voice search trends in Southeast Asia are changing how people search for information, no longer typing short keywords, but asking questions directly as if talking to a friend. Because asking questions via voice is more natural and culturally contextual, SEO can no longer focus solely on rigid keywords. Brands must understand how users in this region mix languages, use local slang, and even incorporate religious or polite elements into their questions.
Technical SEO for voice search is now the new foundation for staying competitive. Businesses that adapt their content structure to conversational questions, use the right schema markup, and perform deep localization will appear more easily in voice search results. If you want to optimize multilingual content automatically and SEO-friendly without creating many manual versions, Linguise is the most practical solution to get started.




