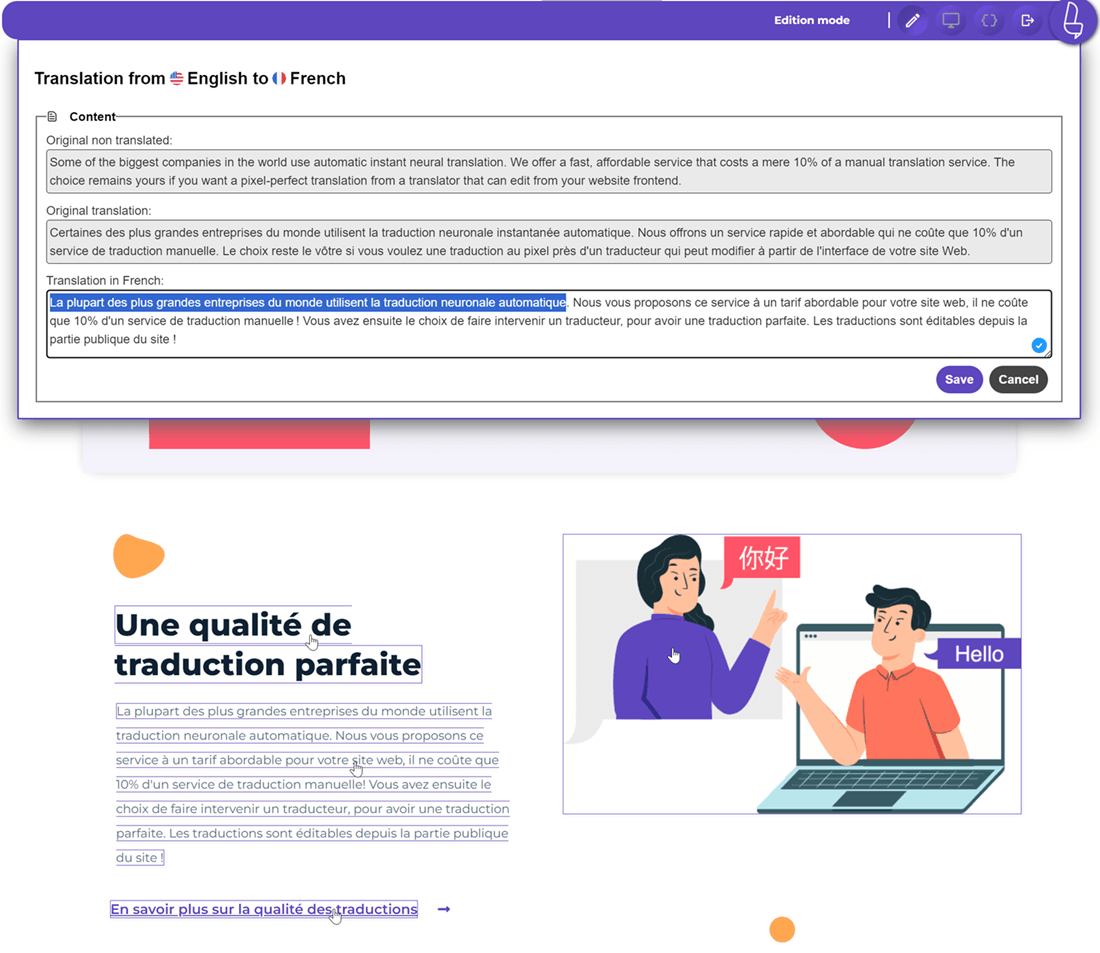
Legal web translation is essential for organizations expanding globally while staying compliant with international and local regulations. Accurate translation requires not only linguistic precision but also an understanding of regulatory frameworks, privacy laws, and cultural nuances. Errors can trigger legal risks, reputational damage, or compliance penalties.
This article outlines key considerations, country-specific requirements, and best practices to help your team ensure accurate and compliant legal web translation.
Why legal website translation require stricter compliance?

Legal website translation demands more rigorous compliance than general content because errors can have significant legal and financial consequences. Translating legal material involves not just language conversion, but also understanding complex legal frameworks, cultural nuances, and regulatory obligations. Below are the main reasons why stricter compliance is essential.
- Binding legal implications: Legal documents such as contracts, disclaimers, and terms of service carry binding obligations. Any misinterpretation in translation can lead to disputes, penalties, or liability issues for the organization.
- Data privacy and protection requirements: Legal websites often handle sensitive personal information. Compliance with laws like GDPR or CCPA requires careful handling of translations to protect user data and ensure secure processing.
- Official language mandates: Certain countries require legal content to be published in specific official languages. Failure to comply may render legal documents invalid or unenforceable in that jurisdiction.
- Cultural and linguistic nuances: Legal terminology can vary greatly across languages and cultures. Translators must ensure that the intended meaning is accurately conveyed to avoid ambiguity or misinterpretation.
- Cross-border regulatory complexity: Multilingual websites must adhere to different regulations in each country. Stricter compliance ensures that translated content meets local legal standards while maintaining consistency across regions.
Key legal considerations in website translation

When translating a legal website, organizations must pay attention to several critical considerations to ensure compliance, accuracy, and legal validity. These key factors guide translators, compliance teams, and localization managers in creating multilingual content that adheres to both local and international regulations.
Accuracy and faithful representation
Ensuring that the translated content accurately reflects the original legal text is paramount. Even small errors or omissions can lead to misinterpretation of legal obligations, resulting in disputes or liability issues. Translators must be highly familiar with legal terminology and context to maintain the integrity of the information.
Additionally, having a review process with legal experts can further reduce the risk of inaccuracies, ensuring that every translated page conveys the same legal meaning as the source content.
Confidentiality and data protection
Legal websites often contain sensitive information about clients, contracts, or internal policies. Maintaining confidentiality during translation is essential, which includes using secure file transfers, encryption, and vetted translation partners. Compliance with data protection laws such as GDPR and CCPA is a critical part of this process.
Beyond technology, organizations should also implement strict internal protocols to limit access to sensitive files, ensuring that only authorized personnel handle legal content.
Official language compliance
Many jurisdictions require legal content to be published in one or more official languages. Failing to comply with these requirements may invalidate legal documents or expose the organization to fines. Translators must be aware of which languages are legally recognized in each country where the website is accessible.
It is also important to monitor updates to official language regulations, as countries can change requirements over time, which could affect previously translated content.
Consistency in terminology
Consistency in legal terminology across all translations is crucial to avoid ambiguity or conflicting interpretations. Establishing and maintaining a terminology database or glossary ensures that the same legal terms are used uniformly throughout the website.
Regularly updating the glossary and training translators on its use can significantly improve clarity and reduce the risk of misinterpretation, especially when new legal concepts are introduced.
Cultural and jurisdictional sensitivity
Legal norms, conventions, and interpretations can vary between regions. Translators and compliance teams must account for cultural nuances and jurisdiction-specific legal requirements to prevent misunderstandings and ensure the translated content is appropriate for the target audience.
Collaborating with local legal experts or native-speaking translators familiar with regional laws can help ensure that the content is not only accurate but also culturally relevant and legally valid.
Challenges of translating legal terminology and context

Translating legal content is not just about converting words from one language to another; it involves understanding the precise meaning, legal intent, and cultural context behind each term. Legal translators face several challenges that make this process particularly complex and high-stakes.
Language nuances and legal terminology
Legal terminology often has very specific meanings that do not have direct equivalents in other languages. Translators must ensure that terms like “liability,” “indemnity,” or “warranty” are correctly interpreted in the target language to prevent miscommunication. Even slight variations in phrasing can significantly change the legal implications of a document.
Additionally, translators must be aware of context-specific interpretations. A term used in one legal system may carry a different weight or legal implication in another, so understanding both the source and target legal frameworks is essential to maintain accuracy.
Cross-border regulatory differences
Legal requirements vary widely between countries, which can make translating global websites extremely challenging. What is legally required in the U.S., for example, may differ substantially from the European Union or Asian jurisdictions, and failing to account for these differences can create compliance risks.
Translators and compliance teams must stay informed about local laws, official language mandates, and certification requirements in each country. They often need to work closely with legal experts familiar with specific jurisdictions to ensure that the translated content meets all local regulatory standards.
Handling sensitive data in translation
Legal websites frequently handle confidential information such as client records, contracts, or internal policies. Translating this content requires strict protocols to protect data privacy and prevent leaks.
Organizations must implement secure file transfers, encryption, and restricted access policies. Collaborating only with vetted and trustworthy translators is also crucial, as mishandling sensitive data can lead to legal liabilities and reputational damage.
Ambiguity and contextual interpretation
Legal documents often contain language that is deliberately broad or open to interpretation. Translators face the challenge of rendering such content in a way that preserves the original intent without creating new ambiguities.
This requires not only linguistic skills but also an understanding of legal reasoning and context. Review processes and collaboration with legal experts can help ensure that translations are both accurate and legally sound.
Maintaining consistency across multilingual content
For organizations with websites in multiple languages, maintaining consistency in terminology and phrasing across all versions is a major challenge. Inconsistent translation can cause confusion or even legal disputes.
Using terminology databases, glossaries, and style guides can help translators maintain uniformity. Regular audits and cross-checks of multilingual content ensure that all versions of the website convey the same legal meaning and comply with regulatory requirements.
Country-specific legal website translation requirements

When translating legal websites for an international audience, it is essential to consider the specific regulations and language requirements of each country. These rules can vary widely, from data privacy laws to official language mandates, and non-compliance can lead to fines or legal disputes. Understanding the legal landscape of each jurisdiction ensures that multilingual content remains accurate, secure, and enforceable.
United States
In the United States, website translation must consider both federal and state-level regulations. The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is one of the most influential laws, requiring companies to provide transparent privacy policies and ensure that legal terms are accurately translated. Legal terminology such as “personal information” carries precise definitions under U.S. law, which can lead to compliance issues if mistranslated.
Additionally, state-specific regulations, such as stricter standards in New York and Massachusetts for financial and healthcare data, mean that translations must be tailored to local requirements. Organizations need to ensure that translated content communicates obligations clearly to avoid potential liability and maintain user trust.
For example, this section explains the privacy rights of California residents under the CCPA, including the categories of personal data collected and the purposes for which it is used.
European Union
The European Union is governed by the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which sets a high standard for privacy and data protection. Website translations must convey consent mechanisms, user rights, and data handling practices in the official language of the target EU member state. Misinterpretation of GDPR-related terms can lead to significant fines and reputational damage.
Beyond GDPR, the EU emphasizes accessibility and consumer protection. This means that translations should not only be accurate but also easy for citizens to understand, ensuring fairness and transparency in digital communication across all member states.
For example, the opening section, originally referring to Regulation (EU) 2018/1725, has been translated into French to ensure compliance, confirming that this policy has been developed in accordance with EU data protection regulations.

Canada
Canada’s bilingual nature makes language compliance a central issue. The country enforces strict requirements under the Official Languages Act, particularly in Quebec, where the Charter of the French Language mandates that French must be given prominence on websites. Businesses operating nationally must ensure that both English and French content are equally accessible.
Privacy is also regulated through the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA). Translators must carefully handle terminology related to consent, personal data, and user rights to ensure that the translated content aligns with federal privacy standards while also addressing provincial differences.
Example of a privacy policy page about PIPEDA, which has been translated into French for the context of legal web translation.
China
China has specific requirements under the Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) and the Cybersecurity Law, which emphasize the protection of personal data and national security. Website translations must clearly communicate how personal information is collected, stored, and used, especially as Chinese regulators scrutinize foreign companies more closely.
Additionally, websites targeting Chinese users must comply with content restrictions and censorship rules. This means translations should not only be linguistically accurate but also culturally and politically sensitive to align with government standards, ensuring both compliance and market accessibility.
This example shows an NPC Observer displaying the title of the Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) in German (Deutsch), demonstrating how Chinese regulations can also be accessed in multiple languages to support legal translation needs.

Middle East
The Middle East is a diverse region, but countries like the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia have implemented strong data protection frameworks. For example, the UAE’s Data Protection Law requires that privacy terms be communicated transparently in Arabic, while Saudi Arabia’s Personal Data Protection Law also demands clear disclosures.
Cultural sensitivity is equally important in translations for this region. Beyond legal compliance, businesses must ensure that language use respects cultural norms and religious values, as failure to do so can impact both brand reputation and regulatory acceptance.
Here is an example showing part of the official website of the Government of the United Arab Emirates explaining the Personal Data Protection Law, Federal Decree-Law No. 45 of 2021, which has been translated into Italian to provide context on privacy regulations in the Middle East.
Implementation best practices for legal and compliance teams

Translating legal and compliance-related content requires more than just linguistic accuracy, it demands precision, cultural sensitivity, and strict adherence to jurisdictional requirements. Below are some best practices for implementing legal website translations effectively.
Coordinating with certified translators and legal experts
Collaborating with certified translators and legal professionals is crucial for ensuring accurate and compliant translations. Certified translators understand legal terminology and are familiar with country-specific regulations, while legal experts can validate that the translation reflects the correct legal meaning. This partnership helps prevent misinterpretations that could lead to compliance risks.
For example, when translating a privacy policy for the European Union under GDPR, a certified legal translator can ensure the terminology matches the regulation, while a compliance lawyer confirms that the policy aligns with EU legal requirements. This dual verification process adds a strong layer of protection.
Integrating translation technology and multilingual CMS
Using translation technology, such as translation memory (TM) and terminology databases, helps maintain consistency across legal documents. A multilingual Content Management System (CMS) allows organizations to manage content efficiently, ensuring updates are quickly reflected across all translated versions.
For instance, a global company operating in both Canada and France can use a multilingual CMS integrated with translation tools to ensure that updates in English are automatically flagged for translation into French. This minimizes the risk of outdated or inconsistent legal content across languages.
Setting up internal review and terminology management processes
An internal review process is essential to validate translations before publication. This includes quality assurance (QA) steps such as proofreading, consistency checks, and terminology management. Creating an internal glossary of approved legal terms ensures that translations remain consistent across documents and jurisdictions.
As an example, a compliance team managing employment contracts across Asia could establish a terminology list for terms like “employee rights” or “termination clause” to ensure they are translated consistently into Japanese, Chinese, and Korean. This prevents confusion and reduces legal risk.
Embedding compliance checks in ongoing multilingual workflows
Compliance should not be a one-time task but an ongoing part of multilingual workflows. Embedding compliance checks ensures that every content update or new translation undergoes legal validation. This is especially important in industries with frequent regulatory changes, such as finance or healthcare.
For instance, a financial services company expanding into the Middle East can implement a workflow where a local legal advisor reviews every Arabic translation of new product terms before being published. This ensures both accuracy and compliance with regional banking regulations.
Recommended translation processes and quality checks
Establishing clear translation processes helps streamline legal translation projects. Best practices include assigning roles (translators, reviewers, legal experts), setting deadlines, and conducting multi-step QA checks. A layered review process, first by translators, then by internal reviewers, and finally by legal teams, ensures compliance and accuracy across jurisdictions.
In addition to human review, integrating a reliable translation technology like Linguise automatic translation can significantly improve efficiency. Linguise provides instant, high-quality translations that are optimized for SEO and adaptable to complex legal or compliance-driven content. Moreover, it allows manual human edits directly from the front-end live editor, ensuring that legal nuances, terminology, and contextual accuracy can be fine-tuned without disrupting the workflow.
For example, a U.S. tech company expanding to Germany could combine human and machine workflows, initial translation through Linguise for speed and consistency, review by an internal bilingual staff member, and validation by a certified legal expert to ensure compliance with German labor laws. This hybrid approach balances accuracy, compliance, and scalability, making it easier to maintain quality across multiple markets.
Maintaining continuous updates and regulatory monitoring
Laws and regulations evolve, and so must legal translations. Continuous monitoring of regulatory changes ensures that translated content stays up to date. Legal and compliance teams should set review schedules and track local legal developments in all active markets.
For example, after the introduction of China’s Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL), companies with Chinese websites had to update their privacy policies in simplified Chinese. Regular monitoring allowed businesses to promptly adjust their content, avoiding compliance violations.
Conclusion
Legal website translation is a compliance requirement that determines whether an organization avoids penalties, reputational risks, or even the invalidation of legal documents. Failure to comply with jurisdiction-specific rules can lead to costly fines and serious damage to trust, while accurate and compliant translations build credibility and safeguard legal standing.
By combining certified translators, legal experts, and advanced translation technology, companies can minimize risks while achieving clarity and consistency across multiple markets. Using Linguise’s automatic translation provides a scalable, SEO-friendly, and instant multilingual solution that supports compliance without sacrificing efficiency. In the end, success in legal website translation equals compliance, trust, and global growth, ensuring organizations confidently expand while staying aligned with evolving international regulations.