Language bias is the use of language that unfairly disadvantages or stereotypes certain groups of people. This bias can be explicit, with the blatant use of discriminatory language, or implicit, subtly woven into terms and phrases that appear neutral.
Intentional or not, language bias can have significant consequences. It can alienate individuals, hinder communication, and even perpetuate inequality. Therefore, it is important to address this issue to minimize more widespread language bias.
What is language bias?
Language bias refers to the tendency to favour or discriminate against certain groups in language usage. This can manifest in words, phrases, or expressions that unintentionally marginalize, belittle, or offend individuals or groups based on their identities, such as gender, race, age, abilities, or other backgrounds.
Language bias often stems from outdated social norms and a history of oppression against certain groups. Although not always intentional, biased words and phrases can convey hidden messages of superiority or inferiority of one group over another.
Biased language can reinforce negative stereotypes and make sure groups feel unappreciated or marginalized. Therefore, it is essential to avoid language bias to make our communication more inclusive, fair, and respectful of diversity.
Avoiding language bias helps create an environment that is more accepting of differences. By using inclusive and impartial language, you demonstrate your concern for everyone, regardless of their diverse backgrounds.
6 types and examples of biased language
Language bias and biased language are often confused but have distinct meanings. Language bias is a general tendency to favour those who communicate similarly to us. Biased language refers to words that can be harmful or exclusionary due to neglecting aspects of someone’s identity.
So here are types of biased language and some examples.
Gender bias
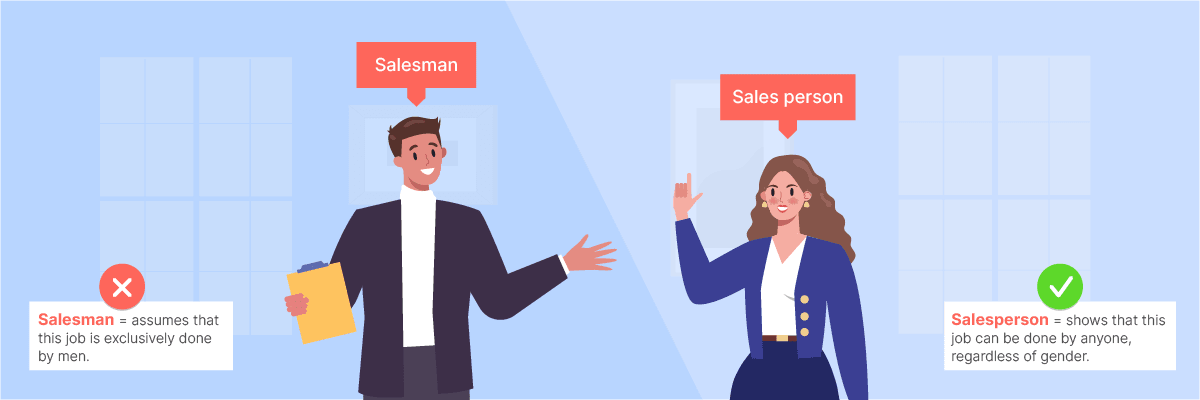

Gender bias in language refers to the use of words, phrases, or structures that discriminate against or belittle one gender. This often appears in assumptions and gender stereotypes embedded in our daily language.
For example, in English, many terms default to using masculine nouns, such as “mankind” and “man-made.” Additionally, many professions are assumed to be male-dominated, such as “fireman” and “salesman.”
To avoid gender bias, we need to use more inclusive and neutral language. For instance, using “humanity” instead of “mankind,” “firefighter” instead of “fireman,” and the pronouns “they/them” instead of “he/him” or “she/her.”
Age bias

Age bias in language refers to using words or phrases that belittle or generalize people based on age. This often occurs in condescending labels towards older individuals or the elderly.
For example, terms like “the elderly,” “old man/woman,” or “senior citizen” can sound demeaning and fail to show respect for the individuals they describe.
Cultural bias

Cultural bias in language refers to using words or phrases that make assumptions or generalizations about someone based on their cultural background, language, or appearance. This often occurs through comments or questions that imply someone is considered “not from here” or “foreign.”
For example, they are using terms like “people of color” or “dark-skinned people” instead of specifying their racial or ethnic identity. This generalizes many different cultures solely based on skin color.
Racial bias


Racial bias in language refers to the use of words or phrases that offend or discriminate against someone based on their race or ethnicity. This often occurs in the form of negative stereotypes, the use of racist language, or language implying the supremacy of a particular race.
For example, assuming someone’s language proficiency is based on race, such as “Your English is very good for an immigrant.” Another example is describing someone’s qualities or characteristics based on race, such as “He’s very intelligent for a black person” or “It’s no surprise she’s selfish, she’s Asian.”
Disability bias

Disability bias in language refers to the use of words or phrases that belittle or discriminate against people with disabilities or specific health conditions. This often occurs in language implying that they are “less capable” or “incomplete.”
For example, they are describing someone who uses a wheelchair as “confined to a wheelchair” or referring to someone with a particular illness as a “victim” of that illness. This implies that they are helpless and unable to achieve success or happiness like others.
Religious bias


Religious bias, or bias based on religion, refers to the use of language that discriminates against or belittles groups or individuals based on their religious beliefs. For example, mentioning someone’s religion or religious identity in an irrelevant or out-of-context manner can trigger stereotypes, such as “That Muslim prosecutor…”
Effect of language bias
Language bias has significant impacts, both at the individual and societal levels. Below are some adverse effects that can arise from the use of biased language.
Inaccuracy
Inaccuracy is one of the most severe impacts of language bias in translation. Both human translators and machine translators with specific language biases tend to interpret and translate content according to their perspectives, values, or personal beliefs.
The consequence of inaccurate translation can lead to misunderstandings and the dissemination of incorrect information to readers. Therefore, translators must be vigilant about their language biases and strive to translate content as accurately as possible according to the original intent.
Perpetuating discrimination against certain groups
The use of biased language in translation content can be seen as a justification or legitimization of discrimination and hostility towards certain groups. For example, if a translation uses racist terms such as “negro” or “slant-eye,” it can perpetuate racism and hatred towards racial/ethnic groups because it is considered “normal” or “acceptable.”
Causing misunderstandings and cultural conflicts
Language bias in translation can also lead to misunderstandings and cultural conflicts between readers and the original culture of the content. For instance, if a translated tourism website uses biased language towards a particular local community, it can trigger discomfort or conflicts between tourists and the local community. This can hinder cross-cultural understanding and efforts to foster positive intercultural relationships.
Impact on acceptance
When readers detect bias in translated text, it can immediately reduce the overall credibility of the content in their eyes.
Readers may question the objectivity and accuracy of the translation, ultimately leading them to doubt the truthfulness of the information presented. For example, suppose readers find that the translator uses language or phrases favouring one side in a translated article. In that case, this can lead them to perceive the entire article as biased and unbalanced.
If readers feel their perspective needs to be more fairly represented, confident readers may refuse to accept the content.
How do we avoid language bias?
Now that you know what language bias is, the types, and the effects that may arise if language bias is left unchecked. Therefore, you must know how to avoid language bias to prevent it from occurring in website translations or your language writing.
Use a third person's point of view
When a writer uses first-person plural pronouns such as “we,” “us,” and “our,” these words assume that the reader shares the same experiences or perspectives as the writer. Since this is not always the case, it is better to use third-person pronouns.
For example:
❌ We found that this law disrupts classroom management.
✅ Teachers found that this law disrupts classroom management.
Compare carefully
When writing about a group of people or making comparisons between groups, make sure to be specific and avoid unnecessary generalizations. You need to choose your words carefully in your writing so that readers do not feel like they are reading your personal opinion. Words such as “bad,” “better than,” “worse than,” and so on indicate your bias to the reader.
For example:
❌ Company ABC, better than XYZ, distributes profits to its employees.
✅ Company ABC distributes profits to its employees, which are unavailable at company XYZ.
Be specific when writing about a group of people
When writing about a group of people, you can avoid bias by being as specific as possible rather than just using general terms that could be potentially offensive.
For example:
❌ older adults often experience health problems.
✅ Adults in their 60s and 70s tend to face particular health challenges, such as osteoporosis or high blood pressure.
Be empathize
For those who haven’t experienced discrimination, it can be challenging to realize the impact of insensitive language. However, for those who are frequently discriminated against, coarse language can exacerbate their experience. To understand this, it’s important to empathize with others’ experiences. In doing so, we can pay more attention to the language used to respect others’ feelings.
For example:
When a manager criticizes an employee’s performance in front of their colleagues without providing adequate feedback or support, it may be difficult for a manager who has never experienced such treatment to realize how hurtful the experience is for the employee. Therefore, assume the employee’s position and imagine how they would feel in the same situation. By doing so, the manager can choose their words more wisely and respect their employees’ feelings.
Use gender neutral
When selecting words, avoid using those that indicate preference or bias toward a particular gender. Use gender-neutral terms if possible to refer to individuals or groups. Instead of using specifically gendered pronouns, consider using “they” or “them.”
For example:
❌ The salesman demonstrated the product to the customers.
✅ The sales representative demonstrated the product to the customers.
Provide evidence
Include relevant evidence or references to support your arguments when making claims or statements. This helps reduce the likelihood of bias or unsubstantiated assumptions.
For example:
❌ Eating a balanced diet contributes to overall health.
✅ According to a survey conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), adults who consume five or more servings of fruits and vegetables per day are 30% less likely to develop chronic diseases such as heart disease and diabetes compared to those who consume fewer servings.
Seek alternative phrases
Consider alternative words or phrases that are more neutral when encountering phrases or words that may have certain connotations or implications. This is important because using phrases with different assumptions or interpretations can help avoid bias or make some readers feel misrepresented.
For example:
Biased ❌ | Alternative ✅ |
Crazy mentally | Have a mental health condition |
Minorities | Underrepresented communities |
The elderly | People over the age of 50 |
Focus on relevant similarities and differences
When comparing groups or situations, focus on relevant similarities and differences objectively. Avoid generalizations or drawing conclusions that are not supported by facts or evidence.
For example:
❌ The conference was attended by four scientists, two administrators, and a Middle Eastern economist.
✅ The conference was attended by four scientists, two administrators, and an economist.
In the second example, remove the specification “Middle Eastern” from the profession “economist.” By simply referring to “economist,” the focus remains on the role and position of the job held by the individual without adding unnecessary information or potentially eliciting irrelevant stereotypes or assumptions.
Avoid generalizations
Avoid statements that overly generalize entire groups, leading to stereotypes and inaccuracies. Instead, use words like “some,” “many,” and the like to indicate that the described characteristics only apply to some group members, not the entire group.
For example:
❌Women care more about the environment than men.
✅ According to surveys, more women care about the environment than male respondents.
Use live editor translation for better language translation results
Website translation often relies on machine translation, which can produce translations quickly and easily. However, machine translations often need more accuracy and context relevance. Therefore, it’s essential to use direct editing features to ensure the accuracy and clarity of cross-language messages and avoid bias.
Direct editing features can be found on translation services that provide such functionality. Therefore, using web translation services with such features is important to help you avoid bias.
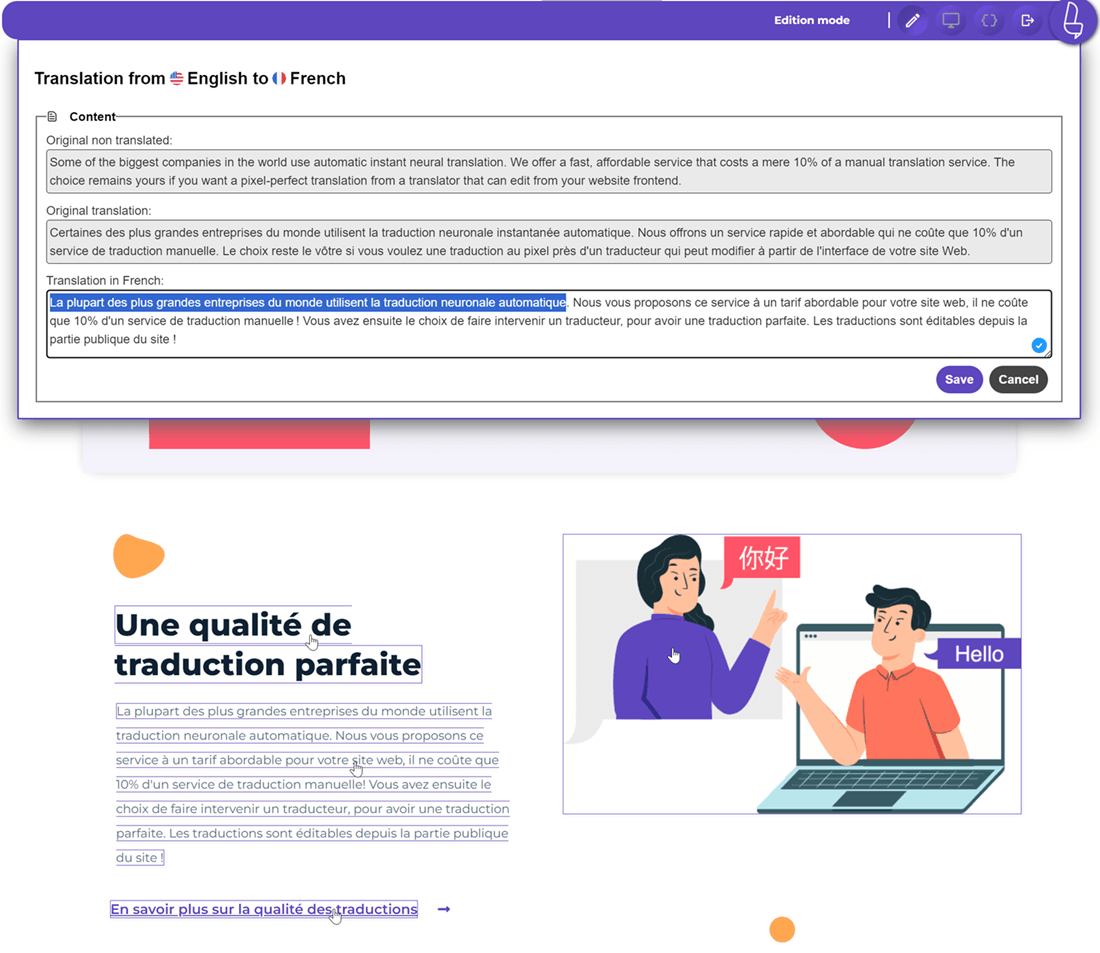
Linguise front end editor to edit translations and avoid bias
If you have a website and want to translate it into various languages, paying attention to the presence of language bias is important. This is solely to provide comfort for readers when viewing your content.
Automatic translation on websites provides quick results, but the results are only sometimes accurate. Therefore, it’s still important to check the results of automatic translation.
Linguise automatic translation offers several outstanding features, including front end live editor.
In this feature, you can modify the machine-generated translation results. You can change them directly on the front page by selecting the desired section. This way, you can see which translation results show bias and can be edited immediately, as shown in the image below.
Linguise has an intuitive user interface so that anyone can use it easily. In addition, other supported additional features include:
- Automatic content detection: Linguise will automatically detect your content for quick and accurate translation into the target language.
- Translate all elements: Linguise can translate all web elements, not just content but also buttons, menus, navigation, forms, and many other components.
- Translation exclusion: translation exclusion feature that can exclude text from the translation you want to leave in its original form or not translated into various languages.
- Multilingual SEO: Linguise supports the implementation of multilingual SEO on websites so that your website’s the potential to be seen by a large audience through search results.
With Linguise, you not only get perfect translation quality of up to 97% but also enable you to edit translation results to avoid language bias.
Try Linguise for better translation results!
Language bias is the unfair or stereotypical use of language that can harm or stereotype certain groups of people. Whether intentional or not, language bias can have significant consequences, distancing individuals, hindering communication, and even perpetuating inequality.
To avoid this issue and minimize widespread language bias, it’s essential to use inclusive and neutral language, avoid generalizations, provide evidence for claims, seek alternative phrases, and focus on relevant similarities and differences when comparing groups or situations. Using live editor translation tools can also help ensure accurate and clear communication across languages while avoiding bias.
Linguise is a translation service that provides editor translations to avoid language bias. If you are interested in using it, register your Linguise account and minimize bias!