Hreflang languages codes are one of the things you need to add to multilingual websites. Hreflang language codes can help the audience find out what web language is currently being used.
Therefore, it is important to determine the right language code with complete guidance regarding hreflang implementation. In this article we will study the list of ISO standard language codes and how to implement them.
What are Hreflang language codes?
For those of you who don’t understand what a hreflang language code is, this is a special HTML attribute that is used to indicate to search engines the language and regional targeting of a particular web page.
This code consists of 2 letters, for example the French code is ‘fr’ and the Spanish code is ‘es’.
These codes allow website owners to define alternative versions of pages for different languages or regions. By implementing hreflang language codes, you can ensure that users are directed to the most relevant version of your content based on their language preferences and geographic location.
The importance of using the hreflang language code means that you must really understand the language code for each country. It is recommended to combine it with the ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 regional hreflang code.
It aims to provide comprehensive information to search engines about the language and geographic region to which a particular web page is directed. Even though they use the same language, spelling and everyday phrases can be different.
List of Hreflang language codes
To help you better understand the list of hreflang codes, we’ve provided a table below based on ISO 639-1, ISO 3166, and common language-country combinations hreflang.
ISO 639-1
Name of language | Hreflang language code |
Afrikaans | af |
Albanian | sq |
Amharic | am |
Arabic | ar |
Armenian | hy |
Azerbaijani | az |
Bashkir | ba |
Basque | eu |
Belarusian | be |
Bengali | bn |
Bosnian | bs |
Bulgarian | bg |
Burmese | my |
Catalan | ca |
Cebuano | cb |
Central Khmer | km |
Chichewa | ny |
Chinese (Simplifed) | zh |
Chinese (Traditional) | tw |
Corsican | co |
Croatian | hr |
Czech | cs |
Danish | da |
Dutch | nl |
English | en |
Esperanto | eo |
Estonian | et |
Fijian | fj |
Filipino | fl |
Finnish | fi |
French | fr |
Galician | gl |
Georgian | ka |
German | de |
Greek Modern | el |
Gujarati | gu |
Haitian | ht |
Hausa | ha |
Hawaiian | hw |
Hebrew | he |
Hindi | hi |
Hmong | hm |
Hungarian | hu |
Icelandic | is |
Igbo | ig |
Indonesian | id |
Irish | ga |
Italian | it |
Japanese | ja |
Javanese | jv |
Kannada | kn |
Kazakh | kk |
Korean | ko |
Kurdish | ku |
Kyrgyz | ky |
Lao | lo |
Latin | la |
Latvian | lv |
Lithuanian | lt |
Luxembourgish | lb |
Macedonian | mk |
Malagasy | mg |
Malay | ml |
Maltese | mt |
Maori | mi |
Marathi | mr |
Mongolian | mn |
Nepali | ne |
Norwegian | no |
Odia | or |
Pashto | ps |
Persian | fa |
Polish | pl |
Portuguese | pt |
Punjabi | pa |
Romanian | ro |
Russian | ru |
Samoan | sm |
Scottish Gaelic | gd |
Serbian | sr |
Shona | sn |
Sindhi | sd |
Sinhalese | si |
Slovak | sk |
Slovenian | sl |
Somali | so |
Sotho, Southern | st |
Spanish | es |
Sundanese | su |
Swahili | sw |
Swedish | sv |
Tagalog | tl |
Tahitian | ty |
Tajik | tg |
Tamil | ta |
Tatar | tt |
Telugu | te |
Thai | th |
Tonga (Tonga Islands) | to |
Turkish | tr |
Turkmen | tk |
Ukrainian | uk |
Urdu | ur |
Uzbek | uz |
Vietnamese | vi |
Welsh | cy |
Western Frisian | fy |
Xhosa | xh |
Yiddish | yi |
Yoruba | yo |
Zulu | zu |
ISO 3166
Country | Alpha-2 code |
Afghanistan | AF |
Albania | AL |
Algeria | DZ |
Andorra | AD |
Angola | AO |
Antarctica | AQ |
Argentina | AR |
Armenia | AM |
Australia | AU |
Austria | AT |
Azerbaijan | AZ |
Bahrain | BH |
Bangladesh | BD |
Belarus | BY |
Belgium | BE |
Belize | BZ |
Bolivia (Plurinational State of) | BO |
Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba | BQ |
Brazil | BR |
British Indian Ocean Territory (the) | IO |
Brunei Darussalam | BN |
Bulgaria | BG |
Burkina Faso | BF |
Cambodia | KH |
Canada | CA |
Chile | CL |
China | CN |
Colombia | CO |
Congo (the) | CG |
Croatia | HR |
Cuba | CU |
Czechia | CZ |
Denmark | DK |
Dominica | DM |
Ecuador | EC |
Egypt | EG |
El Salvador | SV |
Estonia | EE |
Ethiopia | ET |
Finland | FI |
France | FR |
French Guiana | GF |
Gabon | GA |
Gambia (the) | GM |
Georgia | GE |
Germany | DE |
Greece | GR |
Greenland | GL |
Guatemala | GT |
Guinea | GN |
Haiti | HT |
Honduras | HN |
Hong Kong | HK |
Hungary | HU |
Iceland | IS |
India | IN |
Indonesia | ID |
Iran (Islamic Republic of) | IR |
Iraq | IQ |
Ireland | IE |
Italy | IT |
Jamaica | JM |
Japan | JP |
Jersey | JE |
Jordan | JO |
Kazakhstan | KZ |
Kenya | KE |
Korea (the Democratic People’s Republic of) | KP |
Korea (the Republic of) | KR |
Kuwait | KW |
Latvia | LV |
Lebanon | LB |
Liberia | LR |
Libya | LY |
Lithuania | LT |
Luxembourg | LU |
Macao | MO |
Madagascar | MG |
Malaysia | MY |
Maldives | MV |
Mauritania | MR |
Mexico | MX |
Monaco | MC |
Mongolia | MN |
Myanmar | MM |
Namibia | NA |
Nepal | NP |
Netherlands (the) | NL |
New Zealand | NZ |
Nigeria | NG |
Norway | NO |
Oman | OM |
Pakistan | PK |
Palestine, State of | PS |
Panama | PA |
Papua New Guinea | PG |
Paraguay | PY |
Philippines (the) | PH |
Poland | PL |
Portugal | PT |
Puerto Rico | PR |
Qatar | QA |
Romania | RO |
Russian Federation (the) | RU |
Rwanda | RW |
Saint Barthélemy | BL |
Saint Lucia | LC |
Samoa | WS |
San Marino | SM |
Saudi Arabia | SA |
Singapore | SG |
Spain | ES |
Sri Lanka | LK |
Sudan (the) | SD |
Switzerland | CH |
Taiwan (Province of China) | TW |
Tajikistan | TJ |
Thailand | TH |
Timor-Leste | TL |
Turkey | TR |
Turkmenistan | TM |
Uganda | UG |
Ukraine | UA |
United Arab Emirates (the) | AE |
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (the) | GB |
United States Minor Outlying Islands (the) | UM |
United States of America (the) | US |
Uruguay | UY |
Uzbekistan | UZ |
Venezuela (Bolivarian Republic of) | VE |
Vietnam | VN |
Virgin Islands (British) | VG |
Virgin Islands (U.S.) | VI |
Wallis and Futuna | WF |
Western Sahara | EH |
Yemen | YE |
Zambia | ZM |
Zimbabwe | ZW |
Common language-country combinations (hreflang)
Hreflang Code | Language | Country/Region |
|---|---|---|
en-US | English | United States |
en-GB | English | United Kingdom |
fr-FR | French | France |
fr-CA | French | Canada |
es-ES | Spanish | Spain |
es-MX | Spanish | Mexico |
pt-BR | Portuguese | Brazil |
pt-PT | Portuguese | Portugal |
id-ID | Indonesian | Indonesia |
de-DE | German | Germany |
zh-CN | Chinese (Simplified) | China |
zh-TW | Chinese (Traditional) | Taiwan |
ko-KR | Korean | South Korea |
ar-SA | Arabic | Saudi Arabia |
nl-NL | Dutch | Netherlands |
pl-PL | Polish | Poland |
th-TH | Thai | Thailand |
tr-TR | Turkish | Turkey |
vi-VN | Vietnamese | Vietnam |
How to implement hreflang languages codes?
After knowing what the list of hreflang language codes is for each language, next we will discuss how to implement hreflang on a website.
Here there are two ways that we will discuss, namely manually and automatically using one of the website translation services.
Manual implementation with hreflang language code
The implementation guide using hreflang language code involves adding a special <link> tag in the <head> section of the website’s HTML code. A simple example of this code is:
<link rel=”alternate” href=”https://www.yourdomain.com/” hreflang=”en” />
<link rel=”alternate” href=”https://www.yourdomain.com/” hreflang=”id” />
As you probably know, manually implementing hreflang tags can take a lot of time, especially if your website has many pages that require them.
Additionally, we do not recommend the manual approach because it is prone to errors, managing many hreflang tags manually increases the risk of errors, such as inappropriate use of language or country codes, or errors in the hreflang tag format.
Not only that, adding excessive code can slow down page loading times, potentially affecting your website’s SEO ranking.
Such errors can lead to serving content in the wrong language to users, harming the user experience.
HTML head implementation (with x-default)
This is the most commonly used method, where hreflang tags are placed within each webpage’s HTML’s <head> section. These tags inform search engines about alternate versions of the page in different languages and regions.
<link rel="alternate" href="https://example.com/" hreflang="x-default" />
<link rel="alternate" href="https://example.com/en/" hreflang="en-us" />
<link rel="alternate" href="https://example.com/fr/" hreflang="fr-fr" />
<link rel="alternate" href="https://example.com/es/" hreflang="es-es" />
Here is an example of its implementation, as seen in the following image on the right side, there is an alternate rel link equipped with several hreflang codes according to the languages provided by the site.
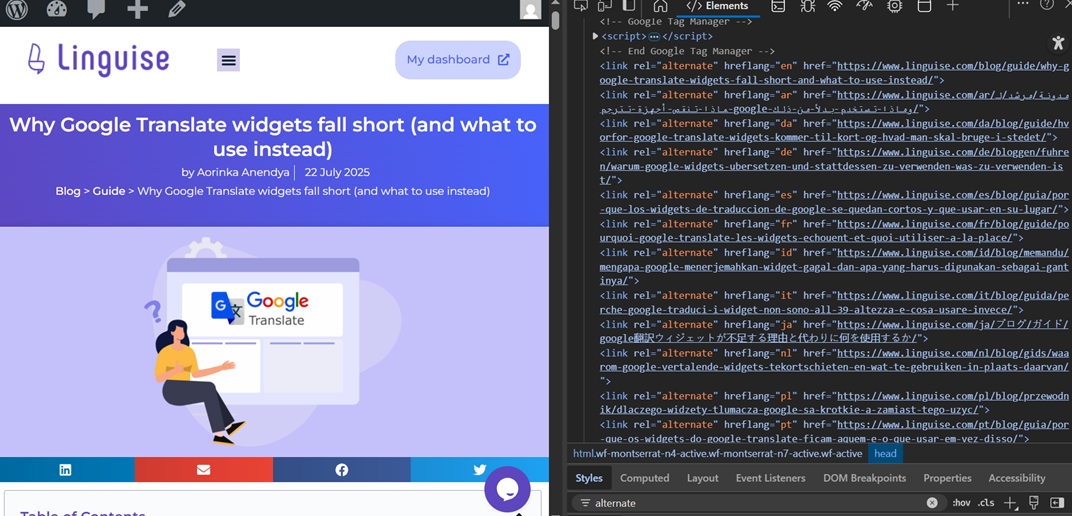
The x-default value is used as a fallback for users whose language preferences don’t match any listed options. It helps avoid misdirected content delivery and improves international SEO performance.
HTTP headers for non-HTML content (e.g., PDFs)
If your site serves non-HTML content like PDFs, images, or downloadable files in multiple languages, you can implement hreflang using HTTP response headers. This ensures that search engines like Google understand which file version to serve based on the user’s language preference, just like they do with web pages.
Unlike HTML pages, where hreflang tags go inside the <head>, for non-HTML content, you define the alternate language versions using a Link header in the server response. To implement hreflang in HTTP headers, you can follow these steps.
- Prepare your file versions, make sure you have a separate file for each language, such as brochure-en.pdf, brochure-fr.pdf, etc.
- Host the files on your own server, upload each version to your website server or CDN, ensuring each has its own public URL.
- Access your server or CDN settings
- Add the Link header manually: Insert the Link header in your server config to declare all alternate versions.
Here’s an example of how it looks:
<https://example.com/brochure-en.pdf>; rel="alternate"; hreflang="en-us",
<https://example.com/brochure-fr.pdf>; rel="alternate"; hreflang="fr-fr",
<https://example.com/brochure.pdf>; rel="alternate"; hreflang="x-default"
Once applied, you can check it via
- Open your file directly in a browser (e.g., https://example.com/brochure-en.pdf).
- Press F12 to open Developer Tools.
- Go to the Network tab and refresh the page.
- Click on the file request, and check the Headers tab to confirm the Link header appears under Response Headers.
XML sitemap implementation
If you prefer a centralized way to manage multilingual URLs, XML sitemaps are a great option. Google and other search engines support <xhtml:link> annotations inside sitemap entries to indicate language and regional versions of the same page.
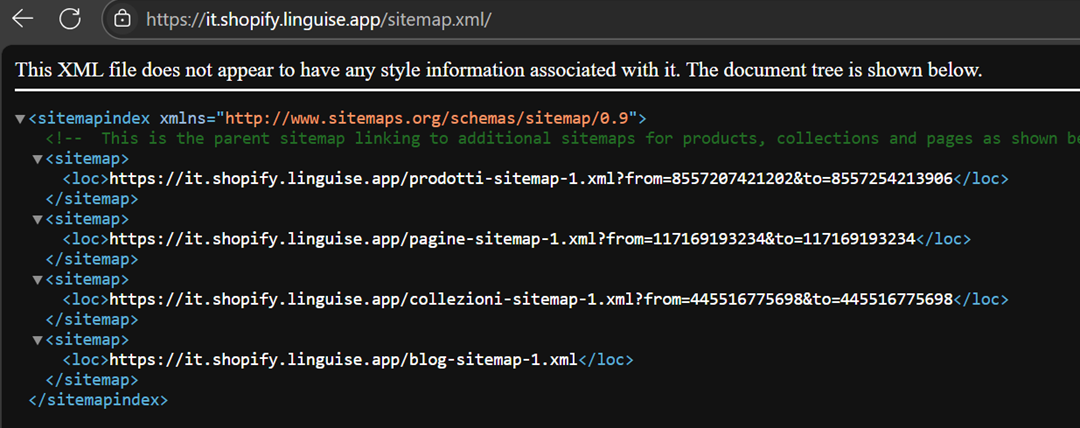
If you are using a multilingual plugin, a multilingual XML sitemap is usually automatically created. Here are two examples of XML sitemaps available in German.
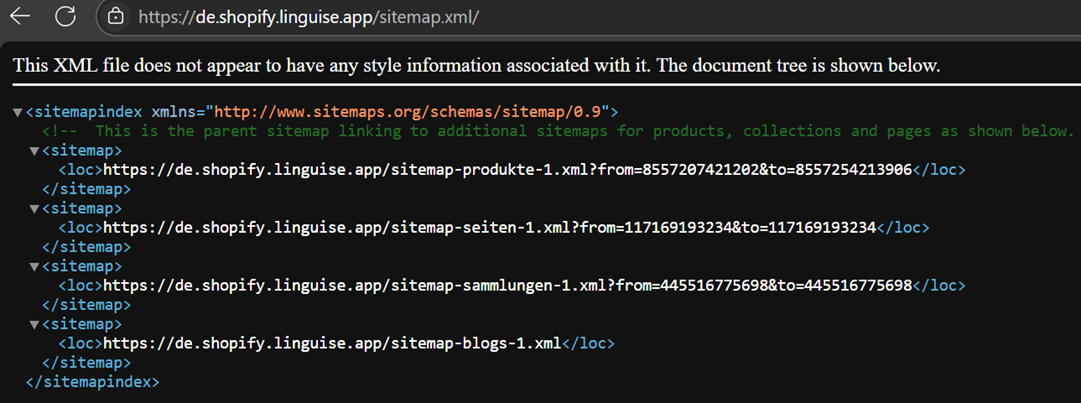
In addition to German, here we also have examples in Italian. So, each language you provide on the website must also have different sitemap pages.
Automatic implementation with Linguise
Linguise offers a solution for automatically implementing hreflang. Using Linguise, hreflang tags can be dynamically adjusted according to the translated content, without the need for manual intervention.
The platform provides automatic translation features and integration with various CMS platforms, helping to reduce the complexity of manual implementation and overcome the risk of errors associated with managing hreflang manually.
Linguise operates by detecting and translating your website’s original content into the target language, then displaying that content without the need to create a site copy.
Simultaneously, automatic hreflang tags will be added to the language and regional versions of your web pages. This process occurs quickly and behind the scenes, without requiring direct intervention in the HTML code.
With Linguise, users can optimize the multilingual display of their websites more efficiently and effectively.
To be able to add hreflang automatically, you need to follow several steps starting from add a website domain. Briefly, the steps are as follows.
- Register Linguise for free
- Add website domain
- Get an API key
- Add language translation
- Setup language switcher
- The website has been translated and the use of hreflang is automatic
After the automatic process you can verify the implementation of the hreflang language tag. To do this, open the page you want to check, right click > Inspect > look at the html lang section at the top left.
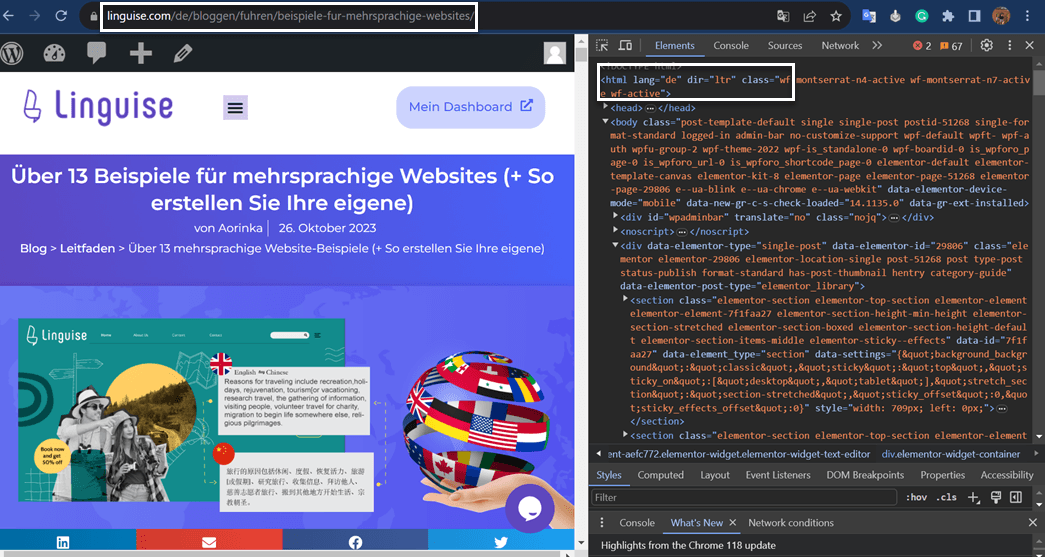
The image above is an example of correct application of hreflang, because the article on the left is using German with the code ‘de’, then when checked, the right side also shows the correct use of the tag, namely html lang=”de”.
If your site has no hreflang tags, fix it immediately so that website content is available in various languages so that it is easier for visitors to understand.
You also need to know that this hreflang language code is also used when you submit a multilingual sitemap to Google Search Console. So make sure the letter code is correct for each language so that it is easy for search engines to crawl.
Tools for hreflang generation and validation

To ensure that your hreflang tags are correctly implemented and optimized, various tools are available to assist with generation and validation. These tools are especially helpful for managing a website with multiple languages or regional versions.
Hreflang.org generator
Developed by SEO experts, this tool supports hreflang tag generation for HTML, HTTP headers, and XML sitemaps.
- Supports advanced configurations like x-default
- Allows you to save and reuse outputs
- Great for large sites with many regional versions
Hreflang.org is especially useful for SEO professionals or developers working on large, complex websites. With flexible output formats, it provides full control over how hreflang tags are implemented across different parts of a site.
Ahrefs Site Audit – hreflang checker
Ahrefs Site Audit is included in Ahrefs’ site audit tool. It helps detect hreflang implementation issues such as.
- Inconsistent tags between pages
- Hreflang pointing to non-canonical pages
- Invalid cross-referencing between language versions
As part of a comprehensive SEO platform, Ahrefs allows you to run deep technical audits and continuously monitor the multilingual SEO health of your site. It’s perfect for businesses and agencies that require regular oversight of hreflang performance.
Screaming Frog SEO Spider
This desktop tool includes a feature to check hreflang through website crawling.
- Verifies hreflang tags in HTML, HTTP headers, and sitemaps
- Provides detailed reports that can be exported
- Ideal for large-scale technical audits
Screaming Frog excels in crawling complex site structures in detail. Its hreflang checker lets you visually inspect all inter-language relationships and instantly detect technical errors that are hard to find manually.
Google Search Console
The last tool is Google Search Console. Although it doesn’t generate tags, GSC helps validate your hreflang implementation.
- Shows errors like missing tags or unlinked language versions
- Works only for sites verified in GS
Google Search Console is a must-have because it shows how Google reads and interprets your hreflang tags. After setup, it’s an ideal companion, offering direct insights from the search engine itself.
SEO benefits of using hreflang code on multilingual sites
As previously explained, it is important for multilingual sites to use hreflang, why is that important?
Because utilizing hreflang code on multilingual sites offers a number of SEO benefits that contribute significantly to the overall performance and visibility of the site. Some of the main advantages include:
- Reduced duplicate content issues: By specifying language and regional targeting, hreflang codes help prevent search engines from flagging identical content across different language versions as duplicate, which can positively impact the site’s SEO performance.
- Improved international search visibility: Implementing hreflang codes allows multilingual websites to appear in relevant search results for users across different regions and languages, leading to increased visibility and traffic from global audiences.
- Better targeted audience engagement: By presenting content in the user’s preferred language, hreflang codes facilitate more targeted and relevant engagement, leading to increased user satisfaction, longer page visits, and improved conversion rates.
- Optimized multilingual content strategy: Hreflang codes enable website owners to develop and implement a comprehensive multilingual content strategy that aligns with the specific preferences and needs of diverse international audiences, ultimately improving the site’s overall multilingual SEO performance.
Conclusion: Automatic hreflang codes with Linguise now!
Now you understand better what the hreflang language code, hreflang list is, and how to implement it both manually and automatically.
To save time and avoid human error, it’s best to use the help of an automated translation service that comes in a package with the use of automatic hreflang.
This way, you don’t need to bother adding hreflang links one by one as many times as there are languages used. Just sign up Linguise, add a website domain, API key relationship, add a language, and automatic translation and hreflang results will be generated. Effective right? Let’s go, try it now!




